What is Leverage and How to use it?
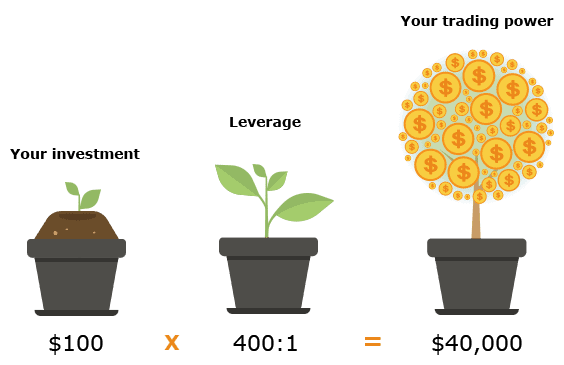
Leverage as it relates to Forex trading is defined as the ability to assume larger positions than would ordinarily be the case as a result of borrowing capital from the broker. In other words it gives you, the trader further trading power on each trade.
In this article we will look at how leverage can both help and hinder your trading. We will look at the relationship between your ever-important margin and the leverage you choose to use. We will also go one step further and explore how to use proper risk management to really use this tool to your advantage. But first let’s start by understanding what leverage is.
-
-
How does Leverage Work?
The basis for leverage is simple: when you have more money to trade, you can potentially make more money for a certain position size than if you did not have this. Being able to trade with $5,000 will give you more profit than if you trade with $500, assuming the trade goes according to your expectation.
If a broker offers a leverage of 1:100, this means that for every $1 you place, the trade now becomes worth $100. So you are effectively amplifying your trading capital.
Example:
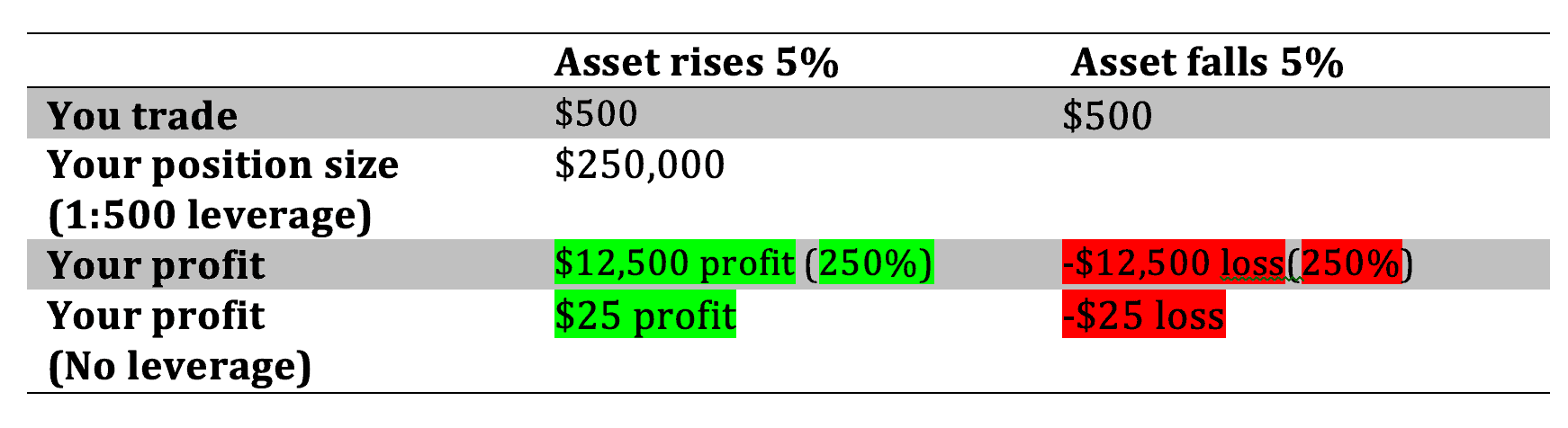
Let’s say you decide to sign up with a new broker called AcmeFX. Now, this broker offers you the trading of currency pairs like the EUR/USD. You open your account with just $500, which is not a huge amount of trading capital, but it’s all you can spare from your salary. You decide to put $500 on trading the EUR/USD. If the EUR/USD gains 5% and you haven’t used leverage, you stand to make only $25 profit. If however, you had used a leverage of up to 1:500 you would now make $12,500 on this one trade. That is a huge difference. So you can see why many traders prefer to use leverage in their trades.
Look at the image below to understand this concept.
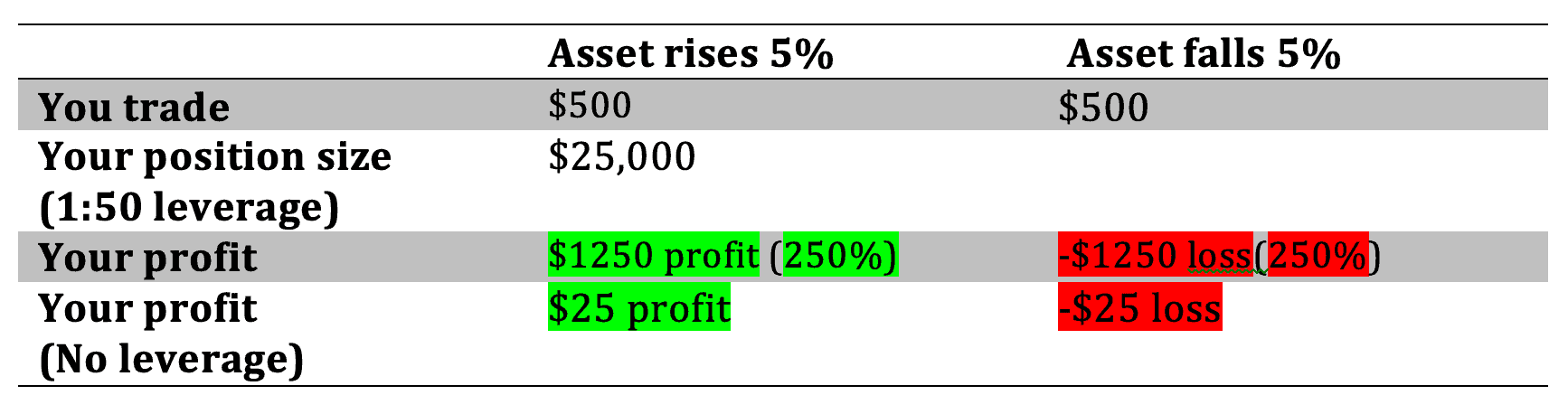
Due to regulation, many brokers cannot offer over 1:50 leverage on the currency pairs for a standard account, or 1:200 for a professional account. The table below shows the same calculations using a leverage of 1:50.
Leverage Means More Reward and More Risk
Leverage is a great feature offered by most of the brokers that you will come across, as it can greatly increase your rewards. It is particularly useful for expert traders or for institutions that would like to magnify their capital outlay. On the flipside though (and there is always a flipside), it can also increase your risk. If you look at the risk warning of most regulated brokers, you will see that around 70%-80% of their traders will lose their money.
So when using the leverage tool on offer from your broker, you must consider the fact that it can ramp up your losses too, and even taken you into negative equity. That means you can stand to lose more money than is in your account.
A good way to negate your account from going into negative equity is to find a broker that offers negative balance protection.How has Regulation Restricted Leverage?
In recent years different regulators have come up with different rules with regards to leverage. This comes after the credit crunch and ensuing recession of 2008. The whole financial sector became one big credit bubble with key players all working on margin or debt. This included banks, traders, and homeowners. It was a house of cards that eventually caved in on itself. The measures taken by regulators are made to ensure that something like this never happens again.
In 2018, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) placed restrictions on the leverage applicable to the trading of forex and CFDs in the UK and the Eurozone. The leverage of Forex brokers applied to major currencies is 1:30, while that of minor currencies and exotics is 1:20. To trade an index CFD, the leverage applied is 1:10 while volatile assets such as stocks will attract a leverage of 1:10. For cryptocurrencies, the leverage is 1:5.
What is Negative Balance Protection?
This is when your broker account is automatically adjusted to zero rather than going to a minus number after a stop out. A stop out happens when all of your active positions are closed down by the broker after your margin level falls below zero.
Before we can really grasp the idea of leverage we need to first understand how you can make money when trading in the Forex market. Let’s start by understanding the concept of margin and its relationship to leverage.
What is a Margin?
Margin is in essence the funds that the trader will need to execute a trade and to keep his position open. It isn’t a cost for the transaction, it’s more like a security deposit for the broker in order to keep the position open. They need to know you have enough funds in your account so you won’t accrue debt that you can’t cover. When you use margin to trade this can increase you exposure, for good and for bad. Margin trading allows you to open up positions larger than what you hold in your trading account by leveraging your funds.
Margin Needed Leverage 2% 50:1 1% 100:1 0.50% 200:1 0.25% 400:1 What is the Relationship Between Leverage and Margin?
You will be required to provide a sum from your capital to serve as the collateral in the trade. This is known as the margin requirement. Whenever a trade is set up, the capital used consists of the trader’s margin, which is a fraction of the total cost, and the leverage provided by the broker. This is reflected in the leverage ratio. So when you see a leverage ratio of 1:100, it means that for every 100 units of capital used in a trade, the trader is required to contribute 1 unit as margin. If a leverage ratio is 1:50, then it means that for every 50 units of capital used in a trade, 1 unit has to be contributed as margin by the trader.
So what is the margin to be used for a Standard Lot trade that is to be setup on the EUR/USD if the leverage provided by the broker is 1:20?
A Standard Lot on the EUR/USD is worth 100,000 units of the account currency, which for most traders is the US Dollar.
If leverage provided is 1:20, it means that the trader must come up with 1 unit for every 20 units of currency used in trade.
Therefore, the margin requirement is (1/20) X 100,000 = 5,000.
So $5000 is required as margin for a Standard Lot trade on the EUR/USD, if the broker provides a leverage of 1:20 for this trade.
As accounts that make use of higher leverage can be affected by larger price swings, this can magnify the chances of triggering a stop loss. That’s why it is even more important to exercise risk management when trading with leverage.
How to Manage Risk When Using Leverage?
- Implement stop loss orders – on every trade you should have a stop loss order in place. You should have calculated this in advance and you should never move your stop loss mid trade unless it is in order to protect a profit.
- Keep your leverage to a minimum – do not use the maximum available leverage as it’s important to keep a cushion again negative price movements. Remember you can ask your broker to use a smaller leverage then they are offering eg. If they are offering 1:100 you can still ask for 1:30.
- Keep to your plan – the best traders all come into their day with a trading plan. They always stick to it, no matter how the market is performing that day. This protects against human emotion like fear or greed, which is one of the greatest enemy’s of the trader.
- Stay updated – it’s a good idea to know what is moving markets from geopolitical events to oil supply. Have an economic calendar to hand to stay on top of the economic events and data releases that can move the assets you are trading. Read the news. The best traders become expert on a small handful of assets, rather than trading a huge variety.
- Don’t overtrade – sometimes the best way to trade, is not to trade at all. Pick your moments, and know that just because the markets are open 24 hours a day does not mean you need to trade those hours.
- Lock in your profit – take profit as often as you can and lock it in. Even locking in partial profits reduces your exposure to the markets. Set take profit orders to help you do this, don’t move these unless you are trying to stop losses.
- Check, and double check – we are only human and human error accounts for the majority of mistakes made when trading forex. Once you’ve set up a trade, check it is in the correct currency, check your stop loss and take profit are at the correct levels.
- Take profit again – this time take profit out of your trading account into your bank or saving account. When funds are in your trading, account you are more likely to continue trading with them. Sometimes the best way to lock away profit is by actually removing it from your trading account.
Remember why you are trading in the first place. Is it to make an income? Some extra funds or for fun? Remind yourself of this and you will take the necessary steps.
Summary: Is Leverage Good or Bad for Traders?
Leverage is the additional capital provided by the broker to enhance the trader’s buying/selling power when trading forex or CFDs on stocks, indices and commodities.
Leverage is a double-edged sword. Profits or losses accrued from leveraged positions are calculated using the enhanced position sizes and not the trader’s margin contribution. All traders must understand the relationship between leverage, margin and position sizing in the ultimate definition of risk management for forex and CFD trading.
A-Z of Forex Trading
Katel
WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up