How to Buy Alibaba Stock For Beginners in 2026
Alibaba is a Chinese online commerce company that matches consumers, merchants, and wholesalers through a single platform. The company went public in late 2014, with its IPO raising just over $21 billion.
It now has a market capitalization of over $520 billion, making it one of the largest companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
In this guide we show you some popular brokers to buy Alibaba stock from, as well as the steps required.
-
-
Where to Buy Alibaba Stock
As Alibaba is now one of the most valuable publicly-listed companies in the US, hundreds of online stock brokers allow you to buy and sell its shares. But when choosing an online stock brokerage from whom you can buy Alibaba shares, you have to put into account such factors as regulations, spreads, commissions, customer support, and payment methods. To help find the right broker, we have reviewed what we consider the best three stock trading websites currently selling Alibaba stocks here:
RECOMMENDED BROKER
What we like
- 0% Commission
- Trade Stocks Via CFDs
- Authorized & regulated by the FCA
Min Deposit
$100
Charge per Trade
Zero Commission
Available Assets
- Total Number of Stocks & Shares+2000
- US Stocks
- German Stocks
- UK Stocks
- European
- ETF Stocks
- IPO
- Funds
- Bonds
- Options
- Future
- CFDs
- Crypto
Charge per Trade
- FTSE 100 Zero Commission
- NASDAQ Zero Commission
- Dax Zero Commission
- Facebook Zero Commission
- Alphabet Zero Commission
- Tesla Zero Commission
- Apple Zero Commission
- Microsoft Zero Commission
Deposit Method
- Wire transfer
- Credit Cards
- Bank Account
- Paypal
- Skrill
Provider Detailed Review
1. Plus500 – Trade Alibaba Stock CFD commission-free
Plus500 is a UK-based broker that accepts investors from numerous countries around the world. Plus500 is also licensed and in multiple jurisdictions including Australia, South Africa, Singapore and Cyprus. Its parent company is also listed on the London Stock Exchange and the online trading platform, Plus500 is authorized and regulated by the FCA. When it comes to investing in Alibaba, you will be doing so via a CFD (Contract-for-Difference).
This means that you will not own the underlying asset, so you wouldn't be eligible for company dividends. With that said, Alibaba is yet to pay dividends to shareholders, so you're not missing out. The upside to CFDs trading is that they allow you to short-sell Alibaba stock, as well as apply leverage. Opening an account with Plus500 takes minutes, and you only need to meet a minimum deposit of $100.
Supported payment methods include a debit/credit card, bank transfer, and PayPal. Plus500 does not charge any trading commissions. However, some of its variable spreads can be expensive, so be sure to trade during standard market hours to keep this to a minimum.
Our Rating
- Fast order execution
- It also allows for commission-free trades
- Access a wide range of trade and market analysis tools
- Stocks only available via CFDs
- Limited research and educational resources
80.5% of retail CFD accounts lose money. Sponsored ad2. Stash Invest – Best USA Broker With Low Deposits
If you're a newbie trader based in the US, it might be worth exploring the merits of Stash Invest. The domestic share dealing broker allows you to open an account by depositing just $5. Additionally, Stash offers fractional shares at no additional cost. This means that you can buy Alibaba stocks with super-low stakes and then diversify the rest of your balance by investing in additional companies.
Unfortunately, Stash Invest does not allow you to deposit funds with a debit/credit card or e-wallet. Instead, you will need to link the app with your US checking account. Stash Invest offers its cheap stock dealing services in return for a monthly fee. This starts from $1 per month for the standard investment account.
If you want all of the features offered by Stash, this goes up to $9 per month. A slight pitfall of using Stash is that you will only have access to the US stock markets. Note also that Stash Invest is a mobile-only stockbroker, so you'll need to have an Android or iOS operating system to install the app.
Our Rating
- $5 minimum deposit
- Allows fractional stock purchases
- Monthly fee from just $1
- Limited number of shares hosted
- No access to international stock exchanges
Sponsored adHow to Buy Alibaba Stock
If you’re looking buy Alibaba stock, below we have listed a step-by-step guide to show you what you need to do. If you’re looking to join one of the other brokers that we have recommended on this page, the process remains largely the same.
Note: As is the case with all regulated stock trading sites, you will first need to open an account and verify your identity. You’ll also need to deposit some funds.Step 1: Search for Alibaba (BABA) Stock
At the top of the screen, you should see a search box. Simply enter ‘ALIBABA’ and click on the corresponding result.
Step 2: Click on ‘Trade’
You will now see a range of information linked to Alibaba, such as historical prices and research tools. Simply click on the ‘Trade’ button and you will be taken to the investment page.
Step 3: Set-Up Order and Buy Alibaba Stock
On the pop-up buy/sell window, set up your trade parameters.
To fill out the order box correctly, read through the following guidelines.
- Amount: Don’t make the mistake of entering the number of shares that you want to buy. Instead, the ‘amount’ box refers to the amount of Alibaba stock that you wish to buy in USD. So, if you want to buy $150 worth of shares, enter this into the box.
- Set Rate: This refers to the price that you wish to enter the market. If you simply want to take the next available price, leave this set to ‘market order’. If you want to specify a particular entry point, change this to ‘limit order’.
- Stop Loss: Stop-loss orders ensure that you mitigate your risks when the market goes against you. You get to specify the price that your Alibaba stocks are automatically sold at. Although not mandatory, we would strongly suggest that you insert a stop-loss order.
- Take Profit: Take-profit orders work in the same way as stop-loss orders but in reverse. As the name suggests, they allow you to lock in your profits automatically. Simply enter your target price into the box.
Finally, click on ‘Buy’ to complete your order.
Why Do People Invest in Alibaba?
You are best advised to perform your own research before investing in Alibaba.
Highly Diversified Business Model
There are a lot of similarities between Alibaba stock and Amazon stock. Not only do the two firms have online retail as their core business model, but they are both highly diversified. For example, much like Amazon, Alibaba is making great strides in the ever-growing cloud computing market.
Similarly, Alibaba also has a stake in the online food and grocery space, albeit, its core focus is in the Chinese market. The company is also increasing its exposure to the digital media sector. This includes sports streaming and a recent licensing deal with Disney.
Unprecedented Growth Continues
We often find that newly listed tech stocks will go through a rapid few years of exponential growth until they reach a plateau. However, this couldn’t be further from the truth in the case of Alibaba. For example, in the company’s most recent earnings report of February 2020, Alibaba reported a staggering 47% increase in quarterly profits.
Not only this, but sales rose by 36%, and its core retail platform attracted an additional 2.5 million customers. These numbers are nothing short of unprecedented, especially when you consider that Alibaba has been trading since 1999.
Huge Cash Reserves
Unlike a number of other tech stocks with multi-billion dollar valuations (think Lyft and Netflix), Alibaba has a super-strong balance sheet. At the time of writing, this amounts to cash reserves of $30 billion, which is huge.
As per the company’s proposed listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, analysts predict that this will raise a further $11-$13 billion to its already beefy balance sheet. This gives Alibaba a huge war chest to continue its diversification strategy and ride out the storm of the Coronavirus pandemic.
About Alibaba Stock
Company and Stock history
Alibaba was launched in 1999 by Jack Ma, a Chinese national who was required to raise $80,000 to start his online e-commerce empire. Fast forward to 2020 and Jack Ma is now one of the richest people in China, with a net worth of $47 billion. Alibaba itself is an online marketplace that seeks to match retailers, wholesalers, and consumers.
Much like Amazon and eBay, sellers that use the platform will pay Alibaba a commission fee when sales are made. Similarly, Alibaba utilizes a rating system that allows buyers to view previous transactions. Although Alibaba is a company based in China, when it went public in 2014 it opted for the New York Stock Exchange.
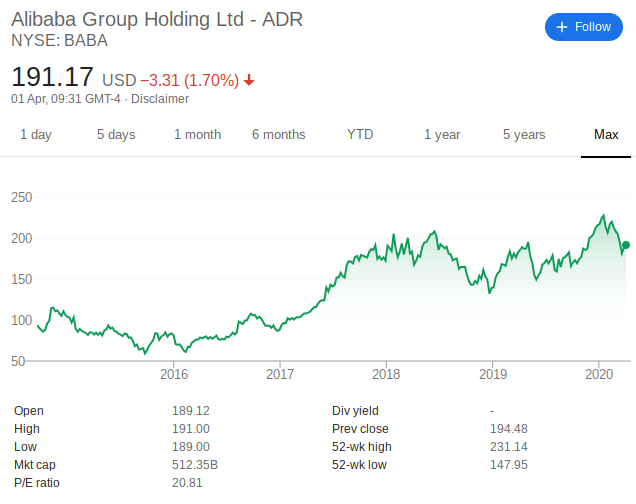
At the time of going public, Alibaba was valued at just over $21 billion, and stocks were sold at $68 per share. Alibaba shares are now worth $194. However, the company has engaged in multiple shares splits since its launch, and its market capitalization now stands at $521 billion.
Alibaba was in an all-time high territory in January 2020 when it hit $227, albeit, the shares have since retreated ever so slightly.
Alibaba Stock
Stock market commentators will often point towards the similarities between Alibaba and Amazon. As we noted earlier, both companies have online retail as their main business focus, and both companies are highly diversified. Although Amazon has strong dominance in this space globally, it is important to remember that Alibaba is involved in wholesale goods, while Amazon targets the retail sector. As such, the two companies are not in direct competition per-say.
Alibaba is still reporting record numbers in the form of operating profits, sales, or customer acquisition, the company continues to soar above the Wall Street expectations. It is also important to remember that Alibaba is in the midst of a huge diversification strategy that has seen it gradually avoid its over-reliance on e-commerce.
This includes large investments in cutting-edge technologies like cloud computing. Even more importantly, if Alibaba can make a success of its online grocery delivery service in China, this could be a game-changer. If you decide to invest in Alibaba stocks, you will only be able to make money via capital gains; this is because the company is yet to distribute dividends to shareholders.
Conclusion
Had you invested in Alibaba stocks back in 2014 when the company first went public, your investment would have grown by over 2,300%. This is an incredible amount of growth to experience in just five years.
With that being said, there is no sure-fire way of knowing just how big Alibaba can get. You won’t be getting any dividends from the company, so you will need to rely exclusively on its stock price smashing through new all-time highs. As such, we would suggest performing your own research on Alibaba prior to parting with your money.
FAQ
How much were Alibaba stocks originally?
During Alibaba’s IPO in 2014, the company listed its stocks at $68 per share. At today’s prices, Alibaba is worth just under $200. However, the company has since engaged in stock splits, so the real-term value is much more than this.
How much cash does Alibaba have?
Alibaba is reported to be sitting on just over $30 billion in cash reserves. It is expected to raise a further $11-$13 billion when it lists on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Does Alibaba pay dividends?
In a similar nature to other multi-billion dollar tech stocks like Amazon and Netflix, Alibaba does not pay dividends. As such, you’ll only be able to make gains through the company’s share price.
Do I need to buy whole Alibaba shares?
Most online stock brokers now allow you to buy fractional shares. If they do, you can invest as little as you wish.
What stock exchange are Alibaba stocks listed on?
Alibaba is listed on the New York Stock Exchange, which is the largest stock exchange in the world.
Who owns Alibaba?
Alibaba is now a publically-listed company, meaning that it is owned by its shareholders. With that said, its founded Jack Ma is still a major shareholder.
Our Full Range of “Buy Stocks” Resources – Stocks A-Z
Kane Pepi
View all posts by Kane PepiKane holds academic qualifications in the finance and financial investigation fields. With a passion for all-things finance, he currently writes for a number of online publications.
WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up