How to Buy and Invest in Mutual Funds in 2020
Mutual funds are making a big comeback. After helpng generations of investors meet their retirement goals, fickle investors have jumped ship to low-cost ETFs and indices. Mutual funds are wooing them back with lower and no fee mutual fund investing. Should you invest?
Here’s why mutual funds still deserve a place in your investment portfolio.
-
-
Our Recommended Mutual Funds Broker for 2020
Our Rating
- Currently Holds Over $2 trillion in Client Assets
- Available To Users All Over the World
- Competitive Rates
- Excellent 24/7 Customer Service
Actively managed funds buy and sell stocks seeking to outperform passive indices. Passive funds replicate the securities in an index to track its performance. As the index holdings and weightings change, the passive fund is adjusted accordingly. Over the long term, passive funds have outperformed active funds, largely due to the higher trading costs of actively managed funds.
Why Should You Invest in Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are investment funds run by professional money managers. They pool the assets of investors and invest them in a portfolio of stocks, indices,
- Choice of active, passive and hybrid investment funds
- Diversification across a portfolio of investments
- Lower trading fees than investing in individual securities
- A variety of investment styles, themes and smart factors to choose from
- Potential for outperformance of stock indices
- Top rated investment managers with performance track records
- Human investment advisory advice may be offered
Mutual Funds vs ETFs
Mutual funds represent 75 percent of the $20 trillion in US open end investment fund assets. The other 25 percent of assets are ETFs, which were not on
the scene 15 years ago. ETFs are a popular low cost investment vehicle. Although mutual funds cost more than ETFs, as fees plummet the cost gap with ETFs is narrowing. If you want to trade low cost investments like stock indices, then ETFs are a better choice. With an ETF, you can trade in and out of your holdings using intraday pricing whenever you want.
A mutual fund, on the other hand, has high redemption fees (e.g., $50 for Fidelity if the fund is sold within 60 days of purchase) and one daily price quote. But keep in mind, low fee ETFs will not provide a cost advantage if you rack up high trading fees. If you are saving for retirement or college, regular contributions to a mutual fund without having to pay trading fees may provide the best value. This cost advantage has made mutual funds the most popular investment product in 401k plans.
Pros and Cons of Investing in Mutual Funds
Pros
- Managed by a professional money manager
- Broad choice of active and passive funds
- No trading fees to make automatic contributions or reinvest dividends
- Large and growing choice of passive index mutual funds
Cons
- Trading fees, management expenses and sales charges may apply
- Portfolio managers not the investor in charge of investment decisions
- Fees and penalties may be charged to withdrawal funds early
Mutual Fund Passive Index Trackers
The story of mutual funds does not end with the arrival of passive ETFs. Instead, a new chapter has begun – the mutual fund index tracker. While actively managed mutual funds have seen a steady decline in assets over the decade, asset flows into mutual fund index trackers is growing at a more robust rate.
The value of the fund closely tracks the index value. Since they do not have high trading or management costs, they are typically low cost funds. Like any index fund, these funds track indices across investment style, regions, sectors and various themes. By eliminating active management and fees, they are levelling the cost advantage with ETFs.
How to Invest in Mutual Funds Online in 2019:
Fidelity - Best Option for US Investors
Mutual Fund Fees: 0.00 pa
Min Deposit: $0
Fidelity has radically transformed its fund business from a supplier of premium fund products and services to one of the lowest cost providers of mutual funds and ETFs. The recent elimination of trading fees and minimum account standards has completed its transformation into a low fee fund broker.
Human investment advisory services have long been a pillar of this leading investment advisor and broker. They include retirement planning, wealth management, and financial planning.
Investment products include mutual funds, ETFs, stocks, options, bonds, and commodities. Buy mutual funds and ETFs quickly through mobile trading or use the advanced trading platform to access real-time pricing, margin trading, short selling and options.
Fidelity offers over 10,000 mutual funds across dozens of fund families.
Choose a mutual fund on Fidelity
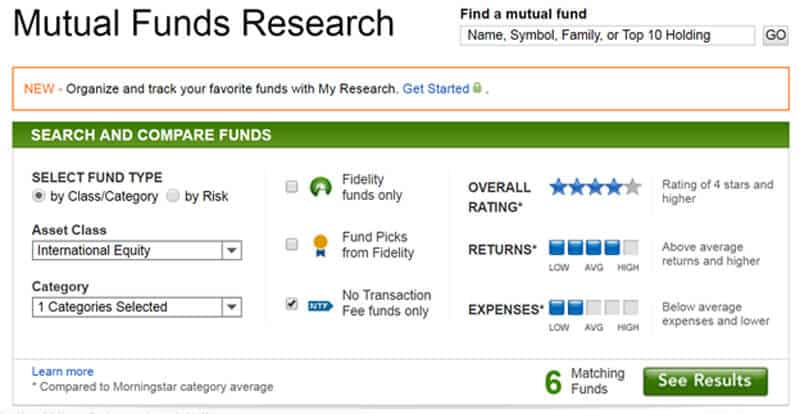
Whether you want to invest in large cap value, small cap growth, a women’s fund or leverage company stocks, you will find a complete universe of investment types at Fidelity. Start your search with the Mutual Fund Evaluator.
- Select Research > Mutual Funds
- Start Search
- Choose the Asset Class, Category and Fund Family. Risk is also an option. Morningstar Rating, Returns and Expenses are additional search criteria.
- Click, See Results
- A list of funds together with performance data, ratings and expense ratios will display.
- Click on funds of interest for a more in-depth profile. Be sure to note the symbol of the funds you want to buy.
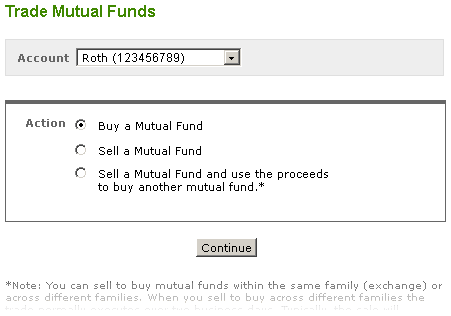
Buy a Mutual Fund on Fidelity Select
- Accounts & Trade > Trade
- Click Trade Mutual Funds
- Click Buy a Mutual Fund
- Enter the mutual fund symbol and dollar amount
- Click Preview Order
- Place Order
Our Rating
- No fees, no account minimums
- Over 10,000 mutual funds to choose from
- Extensive mutual fund research and evaluator tool
- A lengthy set up process
- Lacks a proper online presence
DEGIRO - Best Option for Non-US Investors
Mutual Fund Fees: 2.00 pa
Min Deposit: $0
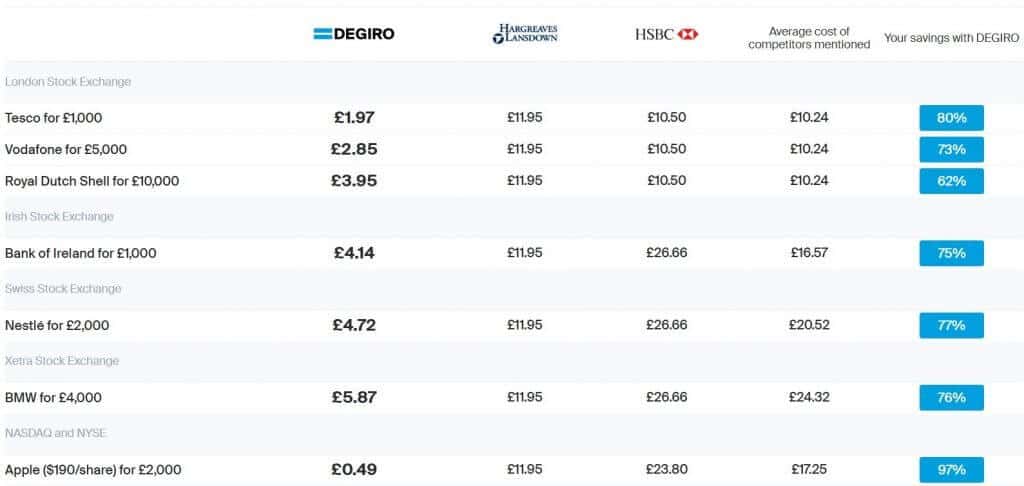
DEGIRO is the fastest growing online broker in Europe. DEGIRO gives investors the tools to be active investors. For $2 a trade, investors gain access to institutional-grade trading on over 50 global exchanges.
Investors can build their own portfolios with access to stocks, bonds, and commodities, and invest in mutual funds and ETFs. This is a no frills service with no research or investment advisory services.
No fee is charged to invest in money market funds through FundShare Cash Funds. A wide universe of listed investment funds is accessed through Euronext Fund Services for a fee of € 7.50 + 0.10% plus a 0.20% service fee.
Choose a mutual fund on DEGIRO
Mutual funds can be bought through Euronext Fund Services.
- Start your search with the Morningstar Fund Screener.
- Select your criteria from the screener, shown in the image. In addition to categories, costs and ratings, search by returns and turnover. Or use a predefined Morningstar Screen.
- Click Set Criteria > Show Results
- A list of funds will display.
Click on funds of interest for a more in-depth profile.
Buy a Mutual Fund on DEGIRO
- Choose the type of product you want to trade > Funds
- Enter the fund symbol
- Enter the order amount
- Enter the share or dollar amount
- Click Place Order
Our Rating
- Low fee trading
- Large universe of investment funds
- Access to global exchanges
- Lacks a widespread online presence
Who Should Invest in Mutual Funds?
- Millennial investor – This young investor wants to save for retirement. He has a longer time horizon and higher risk appetite. Since he does not need the income for many years, he can invest in actively managed mutual funds to seek higher returns. He may choose actively managed mutual funds, high growth stocks, and alternative investments like hedge funds and REITS. Up to 10-20 percent of his portfolio may be placed in these securities.
- Mid-career investor – By mid-life, saving for retirement is an important goal. This investor is seeking not only long-term income appreciation but also investments that will create an income stream in retirement. They include mutual funds invested in dividend paying stocks and interest paying bonds. A large investment advisory firm like Vanguard or Fidelity can also provide related retirement products such as annuities.
- Retirement saver – Mutual funds are a good investment choice when saving for a long-term financial goal. As retirement approaches, the portfolio becomes more conservative. A target-date mutual fund gradually increases the bond allocation and decreases stocks as retirement nears.
What are the Different Types of Mutual Funds?
The large, diversified mutual fund universe allows investors to customize investment portfolios to suit their risk profile and investment goals.
- Equity Mutual Funds
Stock funds may have as many as 3,000–5,000 individual holdings. Not surprisingly, many of the top performing stock funds have ‘growth’ in their name. These mutual funds have tilted their holdings towards growth stocks to produce excess returns above benchmarks. Growth stocks have strong earnings per share and cash flow growth. The T. Rowe Price U.S. Large-Cap Core Growth Fund (TPLGX), one of the highest returning stocks over the past year, has a higher weighting in technology stocks. The FANG (Facebook, Apple, Alphabet, Netflix, Google) Stocks are popular growth kickers in mutual funds. - Fixed Income Funds
Fixed income securities include government bonds and corporate bonds. Government bonds have a very low default rate and thus are investment grade. They provide low but steady returns and are a hedge against a decline in stock prices. Corporate bonds range from investment grade to junk bond. The latter have a high default rate, but in exchange for the risk pay a higher yield. The fund collects the bond interest payments and distributes them to investors. - Balanced Funds
Balanced funds hold a mix of equity and fixed income securities. A conservative balanced fund has a higher weighting in bonds while an aggressive fund has more stocks. - Index Funds
These funds track an index. The value of the fund closely tracks the index value. Since they do not have high trading or management costs, they are typically low cost funds. - Sector/Industry Funds
These funds invest in an industry sector. Or they be diversified across many sectors – for example, cyclical and non-cyclical industries. - Specialty Funds
Specialty funds may invest in commodities or alternative investments such as real estate investment trusts (REITS). Or they may focus on a popular investment theme like socially responsible investing. - Country Funds: These funds invest in securities in one or a portfolio of countries.
- Money Market Funds: Money market funds invest in short-term fixed income securities that can be easily turned into cash. An investor may put emergency money in a money market fund where it earns more than a savings account but can also be liquidated easily if the money is needed. Securities include government bonds, treasury bills, and certificates of deposit. They have lower returns than a stock fund but better returns than a savings account.
- Fund of Funds: Fund of funds invest in a basket of funds. These highly diversified funds may track sectors or themes. An emerging market fund of funds may track index funds tracking various developing economy stock markets.
What are Mutual Fund Fees?
With many different types of mutual fund fees, it easy for the investor to get gouged on fees. Before shopping for mutual funds, take a minute to familiarize yourself with these fees.
- Expense ratio – The expense ratio encompasses the management and operating expenses of a fund. Actively managed, international and small cap funds, for example, have higher expense ratios because they are more expensive to manage. An international artificial intelligence fund will require more research and trading fees to create than a large cap US automotive fund.
- Sales charges – Commonly referred to as load and no load funds, this fee is the commission you pay to buy funds. A Front-end load fee is charged at the time of the purchase of the fund. A Back-end load fund is charged when the mutual fund is sold.
No load funds are typically sold by the fund issuer. Fidelity, for example, does not charge a commission on its own mutual funds but loads are charged for funds of other fund families. - Redemption fees – Many mutual funds charge high fees to sell a fund, especially if the sale is within a short time period after the purchase, say 60 days or under a year. This fee typically declines over time.
Machines have proven that they can invest our money for us, but can they replace human advisers? Robo-advisors match a limited selection of investor profiles with mostly passive ETFs. Actively managed mutual funds apply the expertise and skill of experienced investment managers to buy and sell securities. Active funds often underperform based on solely the fee drag, before investment performance is considered.How to Value Mutual Funds
i) Benchmark: Mutual funds are compared to benchmarks to help investors assess how a fund is performing relative to its peers. A fund may also be compared to an industry benchmark. Index funds directly replicate their benchmarks.
ii) Ratings: Morningstar ratings are the most widely applied ratings of mutual funds. Morningstar ratings are to mutual funds what Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s are to stock ratings. Morningstar rates funds on a scale of 1–5 stars based on risk-adjusted returns.
iii) Fund performance reports: Mutual funds issue semi-annual and annual performance reports. You can access these reports on the mutual fund site or through sedar.com.
iv) Portfolio turnover: Portfolio turnover refers to the frequency at which the fund buys and sells securities. The more trading a fund does the higher the trading fees it occurs. These fees erode the overall portfolio performance. Turnover is measured as a percentage of the average value of a portfolio.
Our Recommended Mutual Funds Broker for 2020
Our Rating
- Currently Holds Over $2 trillion in Client Assets
- Available To Users All Over the World
- Competitive Rates
- Excellent 24/7 Customer Service
Glossary of Investment Terms
BondsA bond is a loan made to an organization or government with the guarantee that the borrower will pay back the loan plus interest upon the maturity of the loan term. It can be advanced to the national government, corporate institutions, and city administration. It is an investment class with a fixed income and a predetermined loan term.
Mutual FundA mutual fund is a professionally managed investment vehicle that pools together funds from numerous investors and invests it in such securities as stocks, bonds, and other money market instruments. They are headed by portfolio managers who determine where to invest these funds. They are highly regulated and invest in relatively low-risk money markets and in turn post lower rates than other aggressive managed funds.
P2P LendingPeer-to-peer lending (p2p lending) is a form of direct-lending that involves one advancing cash to individuals and institutions online. A P2P lending platform, on the other hand, is an online platform connecting individual lenders to borrowers.
BitcoinBitcoin is the legacy cryptocurrency developed on the Bitcoin Blockchain technology. It is a new form of money primarily developed to solve some of the inherent challenges associated with fiat currencies like inflation and over-production. It is virtual (online) cash that you can use to pay for products and services from bitcoin-friendly stores.
Index FundsAn index fund refers to the coming together of individuals to pool in funds that are then invested in the stock and money markets by professional money managers. The only difference between an index fund and a mutual fund is that the index fund follows a specific set of rules that track specific investments and index stocks.
ETFsAn Exchange-traded fund refers to an investment vehicle that is publicly traded in the stock exchange markets – much like shares and stocks. The fund is expert-managed and its portfolio comprises of such investment products as stocks, bonds, commodities, and more money market instruments like currencies.
RetirementRetirement refers to the time you spend away from active employment and can be voluntary or occasioned by old age. In the United States, the retirement age is between 62 and 67 years.
Penny StocksPenny Stocks refer to the common shares of relatively small public companies that sell at considerably low prices. They are also known as nano/micro-cap stocks and primarily include any public traded share valued at below $5.
Real EstateReal Estate can be said to be the land and buildings on a given property as well as other rights associated with the use of the property like the air rights and underground rights. Real estate can be either commercial if the land, property, and buildings are used for business purposes or residential if they are used to non-business purposes – like building a family home.
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)REITs are companies that use pooled funds from members to invest in income-generating real estate projects. While a REIT may specialize in one real estate niche, most diversify and invest in as many high-income real estate projects as possible. They are especially interested in commercial real estate projects like warehouses, prime office buildings, residential apartments, hotels, timber yards, and shopping malls.
AssetAsset simply refers to any resource of value or a resource that can be owned and controlled to produce positive value by an individual or business.
BrokerA broker is an intermediary to a gainful transaction. It is the individual or business that links sellers and buyers and charges them a fee or earns a commission for the service.
Capital GainCapital gains refer to the positive change in the price of a capital asset like shares and stock, bonds or a real estate project. It is the difference between the current selling price of the asset and its lower original buying price and it is considered a taxable income.
Hedge FundA hedge fund is an investment vehicle that pools together funds from high net worth individuals and businesses before having professional money managers invest it in highly diversified markets. The difference between mutual and hedge funds is that the later adopts highly complicated portfolios comprised of more high-risk high-return investments both locally and internationally.
IndexAn index simply means the measure of change arrived at from monitoring a group of data points. These can be company performance, employment, profitability, or productivity. Observing a stock index, therefore, involves measuring the change in these points of a select group of stocks in a bid to estimate their economic health.
RecessionA recession in business refers to business contraction or a sharp decline in economic performance. It is a part of the business cycle and is normally associated with a widespread drop in spending.
Taxable AccountsTaxable Account refers to any investment account that invests in shares and stocks, bonds and other money market securities. The account is offered by a brokerage company and you are obliged to report and pay taxes on the investment income each year.
Tax-Advantaged AccountsA tax-advantaged account refers to savings of investment accounts that enjoy such benefits as a tax exemption or deferred tax payment. Roth IRA and Roth 401K are examples of tax-exempt accounts whose contributions are drawn from after-tax incomes with the yields generated from investing funds therein being tax-exempt. Traditional IRA, 401K plan and college savings, on the other hand, represent tax-deferred accounts. Their contributions are deductible from your current taxable incomes but you get to pay taxes on their accrued incomes.
YieldYield simply refers to the returns earned on the investment of a particular capital asset. It is the gain an asset owner gets from the utilization of an asset.
Custodial AccountsA custodial account is any type of account that is held and administered by a responsible person on behalf of another (beneficiary). It may be a bank account, trust fund, brokerage account, savings account held by a parent/guardian/trustee on behalf of a minor with the obligation to pass it to them once they become of age.
Asset Management CompanyAn Asset Management Company (AMC) refers to a firm or company that invests and manages funds pooled together by its members. Like mutual or hedge funds, the AMC creates diversified investment portfolios that comprise of shares and stocks, bonds, real estate projects, and other low and high-risk investments.
Registered Investment Advisor (RIA)A registered investment advisor is an investment professional (an individual or firm) that advises high-net-worth (accredited) investors on possible investment opportunities and possibly manages their portfolio.
Fed RateThe fed rate in the United States refers to the interest rate at which banking institutions (commercial banks and credit unions) lend - from their reserve - to other banking institutions. The Federal Reserve Bank sets the rate.
Fixed Income FundA fixed-income fund refers to any form of investment that earns you fixed returns. Government and corporate bonds are prime examples of fixed income earners.
FundA fund may refer to the money or assets you have saved in a bank account or invested in a particular project. It may also refer to the collective basket of resources pooled from different clients that are then invested in highly diversified income-generating projects.
Value InvestingValue investing is the art of using fundamental analysis to identify undervalued shares and stocks in the market. It involves buying these shares at the current discounted prices and hoping that a market correction pushes them up to their intrinsic value effectively resulting in massive gains.
Impact InvestingImpact investing simply refers to any form of investment made with the aim of realizing financial returns while positively impacting the society, environment or any other aspect of life in the process. Investment in solar projects and green energy, for instance, posts profits and helps conserve the environment.
Investing AppAn investment App is an online-based investment platform accessible through a smartphone application. It lets you save and invest your funds in a preset portfolio that primarily consists of shares and stocks, bonds, ETFs, and currencies based on your risk tolerance.
Real Estate CrowdFundingReal Estate crowdfunding is a platform that mobilizes average investors – mainly through social media and the internet – encourages them to pool funds, and invests them in highly lucrative real estate projects. It can be said to be an online platform that brings together average investors and lets them enjoy real estate projects previously preserved for high net worth and institutional investors.
FAQs
How much do I need to start investing in mutual funds?
Minimum account balances vary across providers. To invest in funds, Vanguard has a minimum account balance of $1,000. Fidelity has waived its minimum to trade mutual funds. You can buy mutual funds on an automatic investment plan for a set amount a month or quarter. Brokers may provide access to mutual funds with low or no minimum account requirements.
How much are ETF expense fees?
Low cost index funds and ETFs have pushed the price of investment funds down 40 percent over the last decade. In 2018, the average asset-weighted expense ratio was 0.15 percent for passive funds and 0.67 percent for active funds (Source: Morningstar).
Are index mutual funds cheaper than ETFs?
An all out price war among funds has broken out, and investors are the winner. ETFs have the lowest expense fees. But index mutual funds are fighting back. Fidelity has introduced ZERO expense ratio index funds and Vanguard has lowered fees and the minimum investment (to $3,000) to access its lowest cost funds.
Where can I buy the cheapest mutual funds?
Low and no fee online brokers are lowering the cost of buying investment funds. Following are the cheapest fund managers in 2018 (Source: Morningstar Direct Data). Vanguard 0.09 StateStreet 0.17 BlackRock/iShares 0.30 Fidelity 0.48 Invesco 0.60
How can I find cheap mutual funds?
Morningstar provides investor friendly mutual fund screening tools, enabling investors to compare expense ratios and performance across thousands of mutual funds. Most mutual fund suppliers will provide low or no fees on their own funds. Fidelity has recently waived fees on Fidelity funds. Most non-Fidelity funds have a fee of $49.95.
Are mutual funds insured?
Mutual funds are not deposit accounts so they are not covered under deposit safety insurance like your bank account. Your assets are held by a third party custodian. The funds assets are regularity audited by an independent third party auditor. Mutual funds are insured as investment accounts, for example under the SIPC in the US.
Check out our Full Range Of Investment options – Investments A-Z
Maggie Smith
Maggie Smith
Maggie is an investment expert with 10 years experience in dividend stocks and income investing. She has a PhD in Financial Markets and Investment Strategies and has contributed to a number of financial portals, writing stock market analysis pieces and reports on technology stocks and IPOs.View all posts by Maggie SmithWARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up


 the scene 15 years ago. ETFs are a popular low cost investment vehicle. Although mutual funds cost more than ETFs, as fees plummet the cost gap with ETFs is narrowing. If you want to trade low cost investments like stock indices, then ETFs are a better choice. With an ETF, you can trade in and out of your holdings using intraday pricing whenever you want.
the scene 15 years ago. ETFs are a popular low cost investment vehicle. Although mutual funds cost more than ETFs, as fees plummet the cost gap with ETFs is narrowing. If you want to trade low cost investments like stock indices, then ETFs are a better choice. With an ETF, you can trade in and out of your holdings using intraday pricing whenever you want.