Best ETF Brokers 2022 | How To Invest In Etfs | Learnbonds
Investors are joining the passive investing revolution in droves. Fed up with paying high fees to invest in stocks and mutual funds, they are merrily dethroning actively managed funds.
Leading this onslaught is the low-cost and exchange-traded fund (ETF). Because ETFs track an index of stocks or other investments, they do not incur the high costs of buying and selling individual investments.
-
-
M1 Finance App - Best Investing App
Our Rating
- No Fees or Commissions
- No Initial Minimum Deposit
- Beginner Friendly
- Automatic Rebalancing
All investments carry risk - Capital at risk.What are ETFs?
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a basket of securities chosen to replicate an underlying index. They can be diversified across one or several types of security assets (stocks, bonds, and commodities).
Like mutual funds, ETFs are a pooled investment fund that buys/sells shares in a portfolio of investments. But unlike mutual funds, ETFs can be traded intraday like stocks on the stock exchanges.
Why Invest in ETFs?
When you buy ETFs, you do not have to accept the end-of-day price offered by mutual funds. ETFs have the characteristics of shares and stocks, including:
- Real-time trading
- High liquidity
- Long, short and arbitrage positions
- Limit and stop-loss orders
- Fractional trading
- Trading on margin using leverage
Factors setting them apart from Mutual Funds include:
- Lower fees
- More tax advantages
While both exchange-traded funds and mutual funds diversify investment risk across a portfolio of securities, important differences exist. Mutual funds are actively managed by fund managers and thus have higher trading and management costs. Passively managed ETFs track an index and have low expenses.How to Invest in ETFs
This year, investments in passive equity funds, led by ETFs, are expected to surpass investments in actively managed funds. ETF investing has grown alongside the rise of the robo-advisors. With the convenience of mobile trading, they are now readily available both at the exchanges and online.
With an indisputable place in almost any diversified investment portfolio, ETF assets have swelled to over $5 trillion. They are sold by online brokers, banks, large mutual fund suppliers, and via robo-advisors. Online brokers provide one or all of the following ETF investment options.
- Buy and sell ETFs directly like stocks
- Invest in portfolios of ETFs
- Set up an automated program to invest a specified amount at regular intervals in ETFs
- Automatically buy and sell ETFs to rebalance a portfolio
How to Choose an ETF Broker?
While shopping for an online ETF broker, evaluate:
- Number of ETFs – A large number of diversified ETFs makes it easier to develop a diversified portfolio. More importantly, the ETFs should be from reputable suppliers and have good liquidity.
- Credit quality – ETFs are rated like stocks based on their creditworthiness. Morningstar is a reputable assessor of ETFs and mutual funds. The highest-rated Morningstar ETFs have low fees and are broadly diversified.
- Benchmark alignment – The ETF should closely replicate the index it tracks. When the index component changes, the ETF should be adjusted accordingly.
- Costs – In addition to the ETF expense ratio, brokerage commissions will add to your costs.
- Tax implications – If an index does a lot of trading or invests in certain commodities, taxes may be higher. Read the fine print in the ETF prospectus.
- Tax considerations across countries – If the ETF pays a dividend, remember to check the tax agreements with the country the ETF is registered in. In certain countries like Finland, you have to pay tax in the country where the ETF is registered on top of the taxes you normally pay. Source: sijoitusrahastot.orgsijoitusrahastot.org
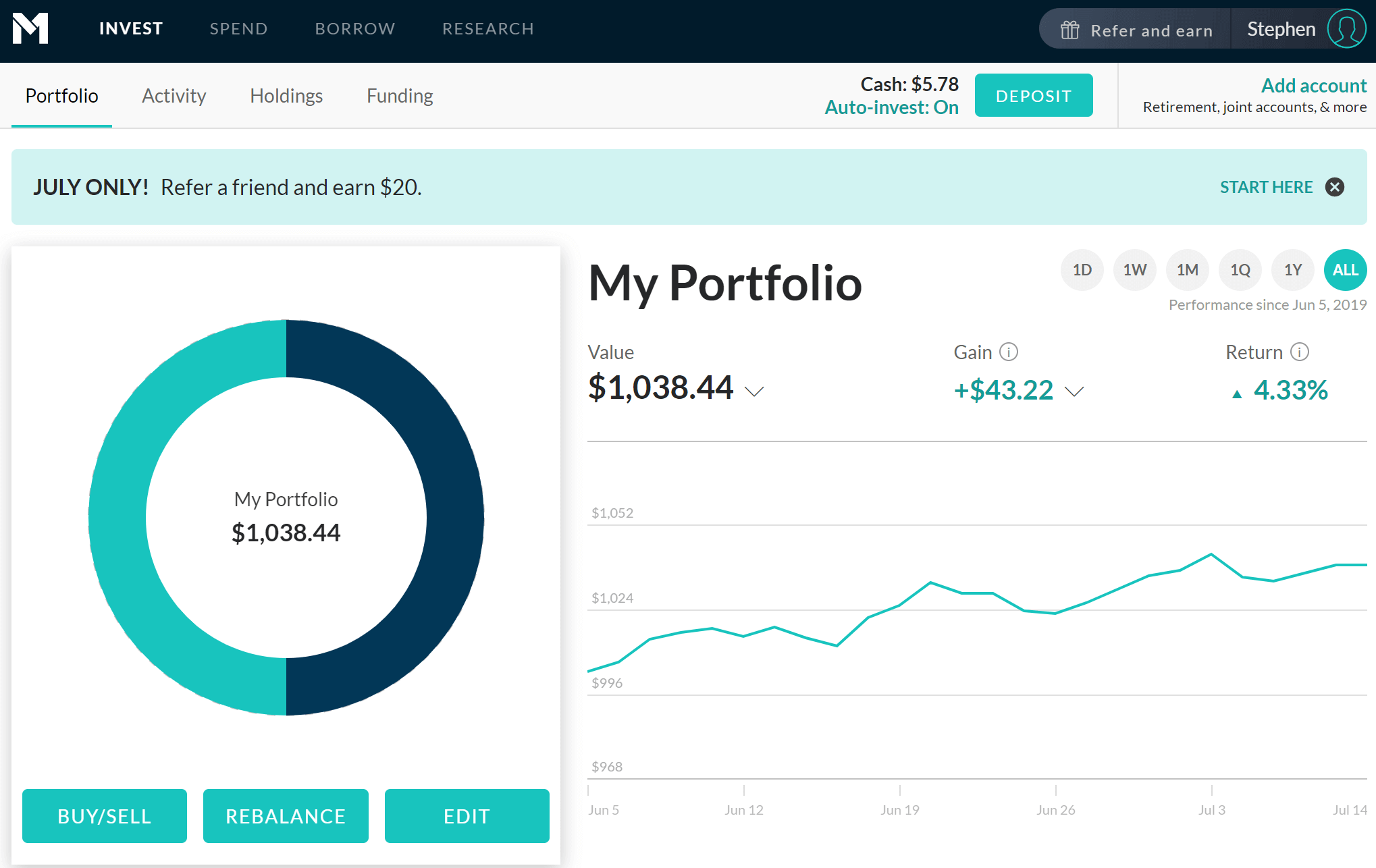
Best US ETF Broker for 2022 – M1Finance
M1 Finance - Best US ETF Broker for 2022
M1 Finance is an ETF supermarket that presents you with a choice of 2,000+ exchange-traded funds. In addition to these are 4,000+ stocks traded on the NYSE, NASDAQ, and BATs.
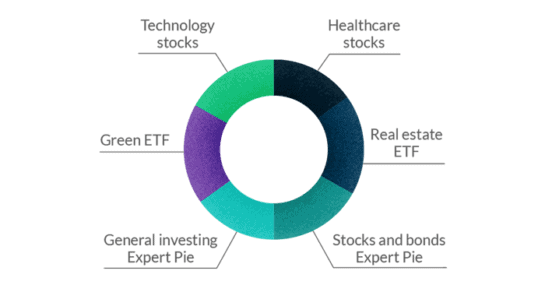
To get started, create a custom Pie of up to 100 ETFs and stocks (referred to as slices). There are no fees or limits on how many pies you can include in your portfolio( note however that ETF expense fees apply).
Once you have created your portfolio, the M1 Finance robo-advisor will automatically buy/sell your holdings to maintain your ideal portfolio balance and within your risk parameters. The robo advisor also grants you access to low-cost margin borrowing, at 4%, that allows you to trade ETFs with leverage.
Additionally, the M1 Spend checking account with debit card sweeps excess cash into investments.
There are three ways to buy ETFs in M1 Finance - Direct Investing, Expert Pies, and Portfolio Rebalancing.
Choose Your Funds
1. From the MyPortfolio screen, click on Add Slice.
2. Choose the Funds tab to display the more than 2,000 ETFs available.
3. Click on the fund you want to invest in.
4. Review the ETF performance and expense fees. 5. Click on Add to Pie to buy the ETF.
6. State the percentage of your portfolio you want this ETF to represent.
7. Save the new portfolio.
Portfolio Rebalancing To allow M1 to automatically buy and sell your ETFs to maintain your portfolio allocation:
1. From My Portfolio, select Rebalance.
2. Select Confirm and M1 will automatically increase the weight of underweight allocations and decrease overweight ones.
Our Rating
- No fees or commissions
- Free automated portfolio rebalancing
- Tax-efficient allocation strategy
- Can be overwhelming for the beginner trader
What to look for in ETFs?
i) A diversified Selection
Some brokers work exclusively with one ETF provider. The ETF selection may be limited and costs higher, but not in all cases. iShares for example, a popular supplier, is among the cheapest ETF providers.
ii) Bid-ask Spread
Spread is the difference between the bid and ask price. A liquid ETF will have a tighter bid-ask spread and be cheaper to buy.
iii) ETF fees and minimum orders
Remember that even no fee brokers have to pass on ETF fees. Compare fees and minimum orders. An ETF provider, for example, may have a $25 minimum.
Types of ETFs
Exchange-traded products track indices (NASDAQ, S&P 500), commodities (the price of gold or oil), and other underlying benchmarks.
ETF Investing by Theme
Here are some popular themes you can track with an ETF:
Industry sectorsDiversified industryCountriesCommoditiesDividendsFixed Income ETFsInvest in a diversified basket of stocks in major industry sectors or target a hot sector (self-driving cars, or robotics). Information technology and healthcare ETFs are currently outperforming other industries.
Over concentration in cyclical industries such as retail and energy that do well when the economy is growing can drag down investment portfolio returns in a slow economy. ETFs tracking indices representing multiple indices such as the S&P 500 diversify this risk. The SPDR S&P 500 Low Volatility UCITS ETF has been a top performer over the last year.
Emerging market stocks benefit from the rapid economic growth of developing economies. By buying a basket of stock indices from different emerging markets, investors can benefit from above-average economic growth while reducing price volatility. China A-shares and Saudi Arabia are top-performing ETFs in the first half of 2022.
ETFs are a good way for the inexperienced investor to invest in commodities without having to use more complex instruments like futures. Both ETFs and futures are ways to invest in physical commodities without having to transport and own the good. An exchange-traded commodity (ETC) is an ETF that tracks a commodity. ETC shares provide fractional ownership in a commodity. An ounce of gold currently costs USD 1,200. One share of the iShares Physical Gold ETC (SGLN) – a top performer over the last six months – represents a 0.020 share in an ounce of gold.
Dividend ETFs invest in dividend-paying stocks. The ETF collects the dividends and distributes them to investors. The investor can accept cash payment or have all dividends reinvested in the ETF.ETFs are democratizing the bond market for retail investors. Although bonds are a part of any diversified portfolio, the choice of bonds has been dreary for individual investors, and mostly limited to government bond funds. You no longer need $10,000 to invest in corporate bonds. An ETF share representing a bond index can be bought for a few dollars. More money has flowed into fixed income than equity ETFs so far in 2022, ballooning bond ETF assets to $1 trillion.ETF Investing by Factors
Factor Investing focuses on strategies known over time to contribute to above-average investment performance. Single and multi-factor ETFs are available. Here are some examples:
- Style – Value vs Growth
A value investor buys stocks trading below their fundamental value with the expectation the price will appreciate in line with its true value. An economic downturn, cyclical industry or supply disruption are examples of events that can lead to temporary declines in a stock price.
- Size – Small Cap vs Large Cap
Small-cap growth stocks have historically outperformed large-cap stocks.
- Volatility – Low Volatility vs High Volatility
Low volatility stocks outperform high vol ones over the long term.
Multi-factor ETFs are growing in popularity. The Xtrackers Russell 1000 Comprehensive Factor ETF (DEUS) is one of the more ambitious multi-factor funds. This ETF covers Quality, Value, Momentum, Low Volatility, and Size factors.
New ETFs
Flexible ETFs are always innovating to give investors more control over their investment returns.
- SoFi’s GIGE fund for the gig economy lets investors in on deals 31 days post-IPO.
- SALT Financial is paying negative interest rates of 5 percent – in other words, paying you to invest in Salt ETFs.
But investors also need to be on the lookout for imitators. Some new products are disguising active funds in ETF wrappers. These fake ETFs plan to compromise some of the features that have made ETFs popular.
- Artificial intelligence ETFs say their bots are so smart they can replace indices, but are these smart bots not machine-learning active investors?
- Non-transparent ETFs aim to report their holdings monthly or quarterly like mutual funds. ETF holdings are always transparent to investors. So you do not have to worry about investing in a value fund and discovering four months later that it has 20 percent of its holdings in declining growth stocks. These opaque hybrid ETFs will be on the market soon.
As a few cheats join the ETF revolution, keep in mind, the real ETF is transparent, tradeable like a stock, and low fee.
ETFs can trade at a slight premium or discount to their underlying indices. Arbitrageurs seek to profit from these discrepancies in prices by taking opposite long and short positions, thereby narrowing any gap in pricing.M1 Finance App - Best Investing App
Our Rating
- No Fees or Commissions
- No Initial Minimum Deposit
- Beginner Friendly
- Automatic Rebalancing
All investments carry risk - Capital at risk.Glossary of Investment Terms
BondsA bond is a loan made to an organization or government with the guarantee that the borrower will pay back the loan plus interest upon the maturity of the loan term. It can be advanced to the national government, corporate institutions, and city administration. It is an investment class with a fixed income and a predetermined loan term.
Mutual FundA mutual fund is a professionally managed investment vehicle that pools together funds from numerous investors and invests it in such securities as stocks, bonds, and other money market instruments. They are headed by portfolio managers who determine where to invest these funds. They are highly regulated and invest in relatively low-risk money markets and in turn post lower rates than other aggressive managed funds.
P2P LendingPeer-to-peer lending (p2p lending) is a form of direct-lending that involves one advancing cash to individuals and institutions online. A P2P lending platform, on the other hand, is an online platform connecting individual lenders to borrowers.
BitcoinBitcoin is the legacy cryptocurrency developed on the Bitcoin Blockchain technology. It is a new form of money primarily developed to solve some of the inherent challenges associated with fiat currencies like inflation and over-production. It is virtual (online) cash that you can use to pay for products and services from bitcoin-friendly stores.
Index FundsAn index fund refers to the coming together of individuals to pool in funds that are then invested in the stock and money markets by professional money managers. The only difference between an index fund and a mutual fund is that the index fund follows a specific set of rules that track specific investments and index stocks.
ETFsAn Exchange-traded fund refers to an investment vehicle that is publicly traded in the stock exchange markets – much like shares and stocks. The fund is expert-managed and its portfolio comprises of such investment products as stocks, bonds, commodities, and more money market instruments like currencies.
RetirementRetirement refers to the time you spend away from active employment and can be voluntary or occasioned by old age. In the United States, the retirement age is between 62 and 67 years.
Penny StocksPenny Stocks refer to the common shares of relatively small public companies that sell at considerably low prices. They are also known as nano/micro-cap stocks and primarily include any public traded share valued at below $5.
Real EstateReal Estate can be said to be the land and buildings on a given property as well as other rights associated with the use of the property like the air rights and underground rights. Real estate can be either commercial if the land, property, and buildings are used for business purposes or residential if they are used to non-business purposes – like building a family home.
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)REITs are companies that use pooled funds from members to invest in income-generating real estate projects. While a REIT may specialize in one real estate niche, most diversify and invest in as many high-income real estate projects as possible. They are especially interested in commercial real estate projects like warehouses, prime office buildings, residential apartments, hotels, timber yards, and shopping malls.
AssetAsset simply refers to any resource of value or a resource that can be owned and controlled to produce positive value by an individual or business.
BrokerA broker is an intermediary to a gainful transaction. It is the individual or business that links sellers and buyers and charges them a fee or earns a commission for the service.
Capital GainCapital gains refer to the positive change in the price of a capital asset like shares and stock, bonds or a real estate project. It is the difference between the current selling price of the asset and its lower original buying price and it is considered a taxable income.
Hedge FundA hedge fund is an investment vehicle that pools together funds from high net worth individuals and businesses before having professional money managers invest it in highly diversified markets. The difference between mutual and hedge funds is that the later adopts highly complicated portfolios comprised of more high-risk high-return investments both locally and internationally.
IndexAn index simply means the measure of change arrived at from monitoring a group of data points. These can be company performance, employment, profitability, or productivity. Observing a stock index, therefore, involves measuring the change in these points of a select group of stocks in a bid to estimate their economic health.
RecessionA recession in business refers to business contraction or a sharp decline in economic performance. It is a part of the business cycle and is normally associated with a widespread drop in spending.
Taxable AccountsTaxable Account refers to any investment account that invests in shares and stocks, bonds and other money market securities. The account is offered by a brokerage company and you are obliged to report and pay taxes on the investment income each year.
Tax-Advantaged AccountsA tax-advantaged account refers to savings of investment accounts that enjoy such benefits as a tax exemption or deferred tax payment. Roth IRA and Roth 401K are examples of tax-exempt accounts whose contributions are drawn from after-tax incomes with the yields generated from investing funds therein being tax-exempt. Traditional IRA, 401K plan and college savings, on the other hand, represent tax-deferred accounts. Their contributions are deductible from your current taxable incomes but you get to pay taxes on their accrued incomes.
YieldYield simply refers to the returns earned on the investment of a particular capital asset. It is the gain an asset owner gets from the utilization of an asset.
Custodial AccountsA custodial account is any type of account that is held and administered by a responsible person on behalf of another (beneficiary). It may be a bank account, trust fund, brokerage account, savings account held by a parent/guardian/trustee on behalf of a minor with the obligation to pass it to them once they become of age.
Asset Management CompanyAn Asset Management Company (AMC) refers to a firm or company that invests and manages funds pooled together by its members. Like mutual or hedge funds, the AMC creates diversified investment portfolios that comprise of shares and stocks, bonds, real estate projects, and other low and high-risk investments.
Registered Investment Advisor (RIA)A registered investment advisor is an investment professional (an individual or firm) that advises high-net-worth (accredited) investors on possible investment opportunities and possibly manages their portfolio.
Fed RateThe fed rate in the United States refers to the interest rate at which banking institutions (commercial banks and credit unions) lend - from their reserve - to other banking institutions. The Federal Reserve Bank sets the rate.
Fixed Income FundA fixed-income fund refers to any form of investment that earns you fixed returns. Government and corporate bonds are prime examples of fixed income earners.
FundA fund may refer to the money or assets you have saved in a bank account or invested in a particular project. It may also refer to the collective basket of resources pooled from different clients that are then invested in highly diversified income-generating projects.
Value InvestingValue investing is the art of using fundamental analysis to identify undervalued shares and stocks in the market. It involves buying these shares at the current discounted prices and hoping that a market correction pushes them up to their intrinsic value effectively resulting in massive gains.
Impact InvestingImpact investing simply refers to any form of investment made with the aim of realizing financial returns while positively impacting the society, environment or any other aspect of life in the process. Investment in solar projects and green energy, for instance, posts profits and helps conserve the environment.
Investing AppAn investment App is an online-based investment platform accessible through a smartphone application. It lets you save and invest your funds in a preset portfolio that primarily consists of shares and stocks, bonds, ETFs, and currencies based on your risk tolerance.
Real Estate CrowdFundingReal Estate crowdfunding is a platform that mobilizes average investors – mainly through social media and the internet – encourages them to pool funds, and invests them in highly lucrative real estate projects. It can be said to be an online platform that brings together average investors and lets them enjoy real estate projects previously preserved for high net worth and institutional investors.
FAQs
How much are ETF expense fees?
Low-cost index funds and ETFs have pushed the price of investment funds down 40 percent over the last decade. In 2018, the average asset-weighted expense ratio was 0.15 percent for passive funds and 0.67 percent for active funds (Source: Morningstar).
Are index mutual funds cheaper than ETFs?
An all out price war among funds has broken out, and investors are the winner. ETFs have the lowest expense fees. But index mutual funds are fighting back. Fidelity has introduced no-fee index funds and Vanguard has lowered fees and the minimum investment (to $3,000) to access its lowest-cost funds.
Where can I buy the cheapest ETFs?
Low and no-fee online brokers are lowering the cost of buying ETFs. No matter which broker you buy ETFs from, you still have to pay the expensive fees. The following are the cheapest funds managers in 2018 (Source: Morningstar Direct Data); Vanguard 0.09, StateStreet 0.17, BlackRock/iShares 0.30, Fidelity 0.48, and Invesco 0.60
Which ETFs are the cheapest?
ETF prices vary across investment themes. Management fees are the largest expense component of an ETF fee. An ETF that tracks the S&P 500 index has among the lowest fees whereas ETFs that invest in alternative investments such as real estate investment trusts (REITS) have the highest fees.
Do ETFs have tax advantages?
ETFs are considered to be tax-efficient if they minimize taxable capital gains contributions and distribute qualified dividends subject to lower taxes. To avoid investments Isley made for tax purposes, ETFs must be held for a specified period for dividend payments to qualify for lower taxes.
What is a margin account?
A margin account allows investors to borrow money from a broker to invest in securities. A broker with 5x leverage allows you to trade 5 times the amount in your account. A $1000 account could trade $5,000. Any gains are multiplied by five, but so too are losses. In the case of losses, a margin call requires you to restore the original value by depositing more money and/or securities in your account.
See Our Full Range Of Investment Resources – Investments A-Z
Maggie Smith
Maggie Smith
Maggie is an investment expert with 10 years experience in dividend stocks and income investing. She has a PhD in Financial Markets and Investment Strategies and has contributed to a number of financial portals, writing stock market analysis pieces and reports on technology stocks and IPOs.View all posts by Maggie SmithWARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up