Derivative Trading | How to Trade Derivatives in 2026
Trading derivatives is a popular way to take your investing to the next level. With derivatives, you can add leverage to your trades, speculate on the future price of non-traditional assets, or create complex trades across currencies. While derivatives add some risk, they can also dramatically increase your returns from investing.
Derivatives can be tricky to understand when you’re just starting out with trading them. In this guide, we’ll explain how you can get started trading derivatives right away and highlight our three favorite brokerages for buying and selling contracts. We’ll also cover the basics about the different types of derivatives that are commonly available so you can better decide what style of derivative trading is right for you.
-
-
Step 1: Open a Derivative Trading Account
The first step in trading derivatives is to open an account with a brokerage that offers different types of contracts. We’ll go into more detail on the different types of derivatives you can trade below. But, when choosing a brokerage, keep in mind that not all brokers offer the same types of derivatives for all the same assets. You’ll need to carefully consider what assets you want to trade and how.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at three popular brokers for derivatives trading.
1. AvaTrade - Popular Platform for Technical Trading
AvaTrade is built from the ground up for technical traders. This platform includes a very powerful custom charting platform that’s chock full of technical studies, drawing tools, and more. Even better, AvaTrade gives all account holders access to the incredibly popular MetaTrader 4 charting software. With this, you’re able to go beyond basic charting to conduct backtests, set alerts, and even develop automated trading strategies. AvaTrade also has a charting-enabled mobile app, which is a major plus for derivative traders on the go.
Derivatives at AvaTrade are largely centered around CFDs. But, the selection of CFDs you can trade is significantly wider. AvaTrade offers contracts for not only forex and commodities, but for stocks, ETFs, stock options, and bonds. CFDs around stock options are particularly interesting, since in this case you’re trading a derivative of a derivative. AvaTrade’s leverage is also quite attractive for risk-tolerant traders—this broker offers leverage of 30:1 on forex CFDs and 20:1 on stock CFDs for retail accounts.
The catch to using AvaTrade is that the brokerage charges a higher spread than many of its competitors in the online CFD trading space. This isn’t entirely surprising given that AvaTrade offers significantly more infrastructure for its users in terms of charting software and asset selection. But, if you’re trying to pinch pennies with every trade, AvaTrade probably isn’t the ideal brokerage for you.
- Derivatives: Stocks, ETFs, Bonds, Stock Options, Cryptocurrency, Forex, Commodities (all as CFDs)
- Demo Account: Yes
- Trade Commissions: No
- Minimum deposit: $100
Our Rating

- Wide Range of CFDs: Everything from stocks to options to forex
- Leverage: Up to 30:1 when trading forex CFDs
- Research Tools: Includes access to MetaTrader 4 and mobile app
- Expensive Spreads: Charges upwards of 0.25% per trade
Sponsored ad2. CryptoRocket - Known for Trading Currency Derivatives
CryptoRocket, as the name suggests, is one of the popular options for trading cryptocurrency derivatives. Whereas most other brokerages offer CFD trading for only the 10 or so most popular cryptocurrencies, CryptoRocket lets traders speculate on the price of dozens of minor cryptocurrencies through CFDs. This broker also supports CFD trading for major forex pairs and widely traded commodities, so it’s far from a one-trick pony. Plus, the platform offers leverage of up to a whopping 500:1 ratio.
One of the things that really sets CryptoRocket apart from other derivative trading brokerages is that you can deposit money into your account as Bitcoin as well as dollars. That makes it an attractive investment platform for traders who are already holding money in digital currencies and want to use that, as opposed to cash, to trade derivatives. There’s no minimum deposit required for CryptoRocket, although you’ll want to be aware of any blockchain fees when transferring money to the brokerage.
CryptoRocket doesn’t slouch when it comes to trading tools, either. You can place trades through the MetaTrader 4 platform, which has real-time price data for all of the currencies traded on CryptoRocket.
- Derivatives: Stocks, Cryptocurrency, Forex, Commodities (all as CFDs)
- Demo Account: No
- Trade Commissions: No
- Minimum deposit: None
Our Rating
- Minor Cryptocurrencies: CFD trading for lesser-known digital coins
- MetaTrader 4: Includes access to research and charting software
- High Leverage: Up to 500:1 for some cryptocurrencies
- Limited Stock Selection: Only 64 stocks available to trade with CFDs
Sponsored adStep 2: Understand Derivatives
Before you dive headfirst into trading derivatives, it’s essential that you understand exactly what you’re trading. There are many different types of derivatives, since they exist for almost every market and it’s possible to create and trade derivatives of derivatives. Here, we’ll take a closer look at four of the most common types of derivatives and how they work.
Contracts for Differences (CFDs)
CFDs are one of the most widely traded types of derivative, in part because they can be easily applied to just about any underlying asset. With a CFD, you are simply speculating on whether the price of an asset will go up or down from the time you purchase the contract. For every percentage point the price of the underlying asset moves up or down, the value of your contract moves up or down a percentage point (or multiple points, if you’ve applied leverage).
CFD contracts are typically written for one month at a time. But, most brokers will roll them over into a new month’s contract free of charge. So, these derivatives are not time-dependent in the way that many other types of derivatives are. Just beware that brokers will typically charge interest fees if you hold a leveraged CFD position overnight.
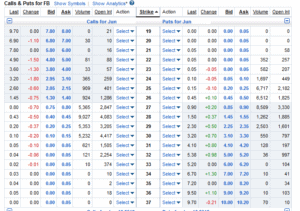
Options
Options are a frequently traded derivative for stocks. With an options contract, you have the option, but not the obligation, to purchase shares of the underlying stock at the price set out in the contract at any time before the contract’s expiration date. You can use options to hedge existing positions or to make highly leveraged bets that the price of the underlying asset will rise above or fall below the strike price of the contract.
Critically, since options expire, their value is heavily influenced by the time remaining to expiration. Take, as an example, an out-of-the-money call option, which gives you the option to buy a stock at higher than its current market price. This unprofitable option is worth a lot less when it’s going to expire tomorrow, as opposed to if it will expire next month and the stock price has time to rebound before the expiration.
Futures
Future contracts are a lot like options, except that you must exercise the contract on the expiration date. You cannot decide not to buy or sell the underlying asset, and your purchase or sale must occur on the contract’s expiration date. Futures are commonly traded around commodities, since farmers, oil companies, and other entities can use these derivatives to hedge their own risk against changing market conditions.
Swaps
Swaps are another very popular type of derivative that are often used to hedge risk or speculate on currency and interest rate markets. With a swap contract, you can, for example, lock in the exchange rate for a currency trade to protect an investment in a foreign currency. Swap contracts can also be used to switch between fixed and variable interest rates, such as on a loan, in order to protect against potential changes in market rates.
Step 3: Choose a Derivative Trading Strategy
Derivative trading carries with it a significant amount of inherent risk. So, it’s important to have a well thought-out strategy to protect yourself and ensure that your trades will be profitable.
There is a huge number of factors to consider when developing a derivative trading strategy, and every trader will have a different approach. But, to help you get started, here are some of the things you should consider when starting to trade derivatives.
Timeframe
The first thing to consider when trading derivatives is what your timeframe will be. For many types of derivatives, and especially options and futures contracts, the timing of price changes in an underlying asset is just as important as the price changes themselves. This doesn’t mean that shorter-term or longer-term contracts necessarily carry more risk, but it’s essential that you have a good idea of when you expect a price change to occur before trading derivatives around that price change.This isn’t necessarily true to the same extent when you’re trading CFDs, since they don’t have a hard expiration date. But, if you’re opening leveraged positions, then time is of the essence since brokers will charge an interest fee every night that your position remains open. Leveraged CFD trades, then, are popular for day traders or intra-week traders.
Technical vs. Fundamental Analysis
Another thing to consider is whether you want to trade based on technical data or fundamental data. Technical data largely focuses on recent price movements and mathematical indicators to try to predict where an asset’s price will be heading next. Fundamental data, on the other hand, looks at supply and demand or company financials for an underlying asset to determine what it’s really worth, regardless of the current asset price.Both approaches have their merits, and many traders use a combination of technical and fundamental trading. But, when trying to put together a derivative trading strategy, it’s important to recognize the differences between these techniques.
Step 4: Open a Derivative Trade
Now that you know how to find a derivative trading brokerage and understand more about derivative trading, it’s time to open a trade. We’ll illustrate the process for opening a CFD position around the price of crude oil. Before getting started, make sure that your account has been opened and funded.
To trade oil CFDs, search for ‘Oil’ in the markets search box. From the oil page, click ‘Trade’ to start setting your trade parameters. Your options are to buy crude oil CFDs if you think the price of oil will rise or to sell crude oil CFDs if you think the price will drop. You can also decide whether you want to apply leverage to your trade to buy more contracts with less money, and whether you want to set an automatic stop-loss or take-profit level. When you’re ready, click ‘Open Trade’ to execute your trade.
Conclusion
Derivatives are frequently used by traders to increase their exposure to a specific asset and to hedge bets on new or existing positions. With derivative trading, you can dramatically increase your return through leverage, but keep in mind that your risk is also multiplied.
Glossary of Trading Platform Terms
Platform FeeThe trading platform fee refers to the amount a trader pays to use the platform and access its integrated platform features and tools. It can be a one –time fee paid for the acquisition of the trading platform, a subscription fee paid monthly or annually. Others will charge on a per-trade basis with a specific fee per trade.
Cost per tradeCost per trade is also referred to as the base trade fee and refers to the fee that a broker or trading platform charges you every time you place a trade. Some brokers offer volume discounts and charge a lower cost per trade for voluminous trades.
MarginMargin is the money needed in your account to maintain a trade with leverage.
Social tradingSocial trading is a form of trading that allows for the interaction and exchange of trade ideas, signals and trade settings between the different classes of traders.
Copy TradingCopy trading, also known as mirror trading is a form of online trading that lets traders copy trade settings from one another. In most cases, it is the newbies and part-time traders that copy the positions of pro traders. The copiers -in most cases - are then required to surrender a share of the profits made from copied trades – averaging 20% - with the pro traders.
Financial instrumentsA Financial instrument ideally refers to the proof of ownership of financial commodities of monetary contracts between two parties. In the money markets, financial instruments refer to such elements as shares, stocks, bonds, Forex and crypto CFDs and other contractual obligations between different parties.
IndexAn index is an indicator that tracks and measures the performance of a security such as a stock or bond.
CommoditiesCommodities refer to raw materials used in the production and manufacturing of other products or agricultural products. Some of the most popular commodities traded on the exchange markets include energy and gases like oil, agricultural products like corn and coffee, and precious metals like gold and silver.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)An ETF is a fund that can be traded on an exchange. The fund is a basket containing multiple securities such as stocks, bonds or even commodities. ETFs allow you to trade the basket without having to buy each security individually.
Contract for difference (CFD)CFDs are a form of contractual trading that involves speculating on the performance of a particular trade in the market. CFD’s will basically allow you to speculate on the future value of securities such as stocks, currencies and commodities without owning the underlying securities.
Minimum investmentThe minimum investment simply refers to the lowest amount of capital injection you can deposit into a brokerage or a trading platform. Different brokers demand varied minimum investment amounts from their clients either when registering or opening trade positions.
Daily trading limitA daily trading limit is the lowest and highest amount that a security is allowed to fluctuate, in one trading session, at the exchange where it’s traded. Once a limit is reached, trading for that particular security is suspended until the next trading session. Daily trading limits are imposed by exchanges to protect investors from extreme price volatilities.
Day tradersA day trader is a term used to describe a trader who is constantly opening trades and closing them within a day. It is a common term used to refer to forex traders who open trade and only hold onto it for a few minutes or hours before disposing and having to leave no open trades at the time the trading day closes.
FAQs
How do CFDs for stock options work?
Some brokerages like AvaTrade allow you to trade CFDs for stock options; a derivative for a derivative. In this case, you’re speculating that the price of the stock option will rise or fall. This is different from simply speculating on the price of the underlying stock, since the price of the option depends on where the stock price is in relation to the strike price and how much time remains until the option’s expiration.
Do I have to trade derivatives using leverage?
When trading CFDs, you can decide to trade with leverage or not. However, other types of derivatives don’t give you a choice. For example, options and futures contracts have leverage built in, and the amount of leverage you’re trading with isn’t constant throughout the trade.
Can I bet against an asset using derivatives?
Yes, derivatives let you speculate that the price of an asset will fall as well as rise. You can sell CFDs if you believe the underlying asset will lose value. For options, you can buy put options if you think the value of the underlying asset will fall.
How much money do I need to start trading derivatives?
There’s no set minimum on how much money you need to trade derivatives other than your brokerage’s account minimum. However, it’s a good idea to have at least several hundred dollars available for trading. This ensures that you can buy more costly CFD and options contracts.
See Our Full Range Of Trading Resources – Traders A-Z
Michael Graw
View all posts by Michael GrawMichael is a writer covering finance, new markets, and business services in the US and UK. His work has been published in leading online outlets and magazines.
WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up