What is Day Trading? Learn How to Get Started
Day traders love price volatility. During the downturn, the passive investor will look to buy cheap value stocks in anticipation of their price appreciating over time. The active day trader will buy long and sell short on significant price movements many times in a day.
-
-
95% of any great trader is going to be risk control. Paul Tudor Jones
You can increase your odds of succeeding as a day trader by having a risk management plan. For starters, consider practice-trading on a demo account for 3–6 months before putting real money at risk in the live markets.
Step 1: Choose a trading platform
1. Tradestation - Hosts comprehensive trading and market analysis tools
TradeStation is one of the most popular brokers with day traders. While the broker has expanded its client base to a more conservative investment crowd, the platform built for speculators is still very popular with day traders.
The trading platform offers futures on stock indices, bonds, currencies, bitcoin, interest rates, and commodities (metals, energy, agriculture). What makes this platform a good starting point for the beginner trader is the choice of mini contracts.
E-minis and micro-minis are offered on stock indices, currencies, and commodities. Margin requirements range from 25–50 percent. If you do hold onto a trade overnight, TradeStation will extend the lower day-trade rate on some instruments.
Additional Information:
- Minimum deposit: $0
- Best feature: Hosts two trading platforms; TS Go for beginners and TS Select for pro traders
- Recommended for: Day traders looking for commission-free trading on most securities
Our Rating

- Runs a highly sophisticated trading platform thats specially designed to suit both beginners and pro traders
- Hosts a wide range of commission free online stock and other tradable securities
- There are no minimum deposits or minimum operating balances on TS Go
- You need a minimum $2,000 to activate the professional TS Select trading account
- Most of the commission-free securities are only available via the TS Select account
Sponsored ad2. TD Ameritrade - Runs a highly sophisticated trading platform
TD Ameritrade is equally popular with active day traders primarily due to its highly affordable trading fees. The online broker for instance doesn’t charge commission for the online stock, options, and ETFs. Not to mention that it supports the trade of a wide range of tradable securities including Forex, futures options, bonds, and even mutual funds.
The online broker also features a highly advanced trading platform that features a host of free but highly sophisticated trading tools. It also features an extensive and free market research tools as well as daily market briefings via live webinars.
These are hosted on the broker’s Think or Swim trading platform in the form of a web trader or a downloadable tool. Additional trading platforms supporting the TD Ameritrade trading platform include the TD Ameritrade mobile web trade iOS app as well as the TDA mobile trader.
Additional information:
- Minimum deposit: $0
- Best feature: The sophisticated Think or Swim trading platform
- Recommended for: Highly active traders looking for most sophisticated trade analysis tools
Our Rating
- No deposit or withdrawal fees, charges $0 commissions and highly competitive trading fees
- Features a highly sophisticated and feature-rich proprietary trading platform
- Easy and straightforward account opening and registration process
- Doesn’t expose you to securities traded on international markets
- One may consider their broker-assisted rates to be exorbitant
Sponsored adStep 2: Learn what is day trading and how it works
What is Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling the same security within the same day with a view to making a quick profit from changes in the price. These intraday traders make money by skimming small profits on high trading volumes. They magnify these profits by borrowing on margin.
- A trader buys 10 CFDs on Apple stock in the morning expecting a positive quarterly earnings announcement in the afternoon and then places an order to sell the stock when the price rises $5. The Apple stock price is $175 (x 10 shares = $1,750], but the trader is only required to pay a 25 percent margin rate (or $43.75 x 10 shares = $437.50). When Apple announces record-blowing iPhone sales, the stock rises to $180 and the limit order is executed for a profit of $50.
- A speculator shorts an e-mini Euro Futures contract when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, with a 2 pip stop-loss. The margin rate is 25 percent of the $1,100 contract. Selling volume spikes and one minute later the trade executes when the price falls 2 pips.
- Algorithmic traders execute in fractions of a second. They develop programs to identify discrepancies in prices across thousands of securities. These clever bots buy and sell securities in milliseconds.
Popular Day Trading Strategies
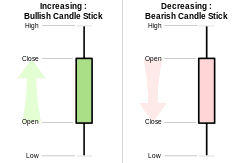
Popular trading strategies have a large influence on price movement. When traders trade the same pattern, they contribute to the sustaining of the pattern. The price intelligence in the simple candlestick provides key price movement indications for many traders.
If this were all there was to trading, we would all be rich. Many other factors can influence price, including economic news, corporate earnings reports, and political events. The largest trades that have the most influence on price are often hidden on dark pools, which allow large traders to trade without exposing their price or volume levels. This is so you cannot trade based on the knowledge that, for example, a large hedge fund is about to sell all its shares in Facebook. If this information were to be made public, all traders would rush to sell their Facebook stock before the inevitable price decline.
i) Trend Trading – The trend is your friend if you can follow it. In an uptrend, trend traders draw diagonal lines upwards that trace higher highs and higher lows. In a downtrend, the descending lines follow lower lows and lower highs. Trading volume is a good indicator of whether or not the trend will continue.
ii) Breakouts – The break out trader uses historical pricing data to forecast future price movements. Price resistance levels are established after the price has reached the same high multiple times (often 3x). Support levels form where the price hits the same lows. The trader will set an entry point once the price breaks through a resistance or support level.
iii) Momentum – The momentum behind a price movement can be an indicator of how much strength is behind a price trend. If the trading volume is strong, the trend is more likely to be sustained while weak trading volume could signal a price reversal.
iv) Pivot Points – These popular price trend indicators take a trading session’s highs, lows, and close to predicting the price trend in the next trading period. The trading period can be on the order of minutes or months.
v) Scalping – Scalpers make money by taking small profits across many trades. They exit as soon as a trade starts losing money rather than wait around hoping the price will reverse. The small gains can add up to a large profit.
vi) Retracement – Prices seldom take off on an upward trajectory without retracing their movements down. Retractors try to predict which retracement signals a large price reversal. They increase their profit potential by buying in the retracement before prices reverse. Fibonacci ratios are popular retracement levels (23.6%, 38.2%, 61.8%).
No strategy is consistently reliable but they can provide an indication of when a price trend is going to continue or reverse. Most day traders combine more than one trading strategy and indicator.
The Day traders Instruments
- Derivatives
Derivatives are used by both day traders and scalpers to bet on the future direction of investment security without paying for the full amount or taking possession of the underlying asset. Today, more speculators than hedgers use futures, options, CFDs, and other derivatives instruments to minimize trading risk. Typically traders borrow on margin to buy futures, options, and CFDs.
- Futures
A future is an obligation to buy or sell a security at a predetermined price and date. The futures price reflects the price of the underlying asset, making it an ideal trading tool. Futures trade on an exchange, significantly lowering counterparty risk. You do have to post an initial margin to trade, which could vary from 0–50 percent or higher.
Mini futures contracts are fractional shares of futures contracts trading on the electronic trading platform of the CME Group. These liquid, low-cost contracts have expanded access to the futures market to the beginner day trader.
E-mini futures – are one-fifth the size of the standard contract of popularly traded stock indices, currencies and commodities
Micro e-mini futures – are one-tenth the size of e-mini contracts
For example, the popular e-mini S&P 500 contract (ES) has an initial margin of $6,930 but can be traded with a day trading margin rate of 25 percent. The Micro ES has an initial margin of $693 and can be traded with a margin of 25% ($173.25).
- Options
An option is a right, but not an obligation, to buy or sell a security at a predetermined price and date. Because options trade separately, they do not always move in tandem with the underlying asset. A large trader may sell short EUR/USD options expecting the US central bank to raise interest rates in the afternoon, thereby pushing the options prices down. The rest of the market may believe the bankers will lower interest rates and are pushing the price of the underlying asset up.
Contract for Differences (CFDs)
A CFD is an agreement between a buyer and seller to trade underlying investment security. Because they trade over-the-counter (OTC) and not an exchange, they pose high counterparty risk. Market data is decentralized. They are considered off-limits by some regulators because they typically use high leverage. How high? The trader may be able to put down 1 percent or less of the contract amount (1:100 leverage).
Binary options are a high risk, high reward trading strategy. A binary option is an all-or-nothing bet on the price direction. If you bet $100 that the price of the USD/GBP currency pair will increase in the next five minutes, you win $100 if the price rises and lose $100 if the price declines. Also known as knock-out or all-or-nothing options, they are popularly used in the forex markets but can be traded on any investment instrument. They are considered gambling and banned by regulators in the US and from retail investors in Europe. Experienced binary options traders do not throw the dice but instead use common trading strategies and technical indicators to forecast the price movement.The old trading adage that timing is everything can mislead the day trader. Instead of focusing on potential entry and exit points to maximize your gains, first focus on ways to minimize your losses. No trader can perfectly time the market. But you can use the one percent rule and position sizing, stop losses, and risk management tools such as futures and options to minimize your downside risk.
Step 3: How to start day trading
Step 1: Start by creating a trader account with the broker
Start by completing the user profile on the site by filling such personal details as your name, email, address. To verify the account, send them your photo and a copy of your government issued identification document.
The broker will also test your day trading experience and ask questions about the amount of disposable income you have at hand.
Step 2: Deposit cash
To activate your account and start day trading the thousands of assets on the platform, you will first need to fund your account.
The minimum initial deposit for any trading account is $50 and you can transfer these funds in in through bank wire, cards, online wallets like PayPal or in the form cryptocurrency.
Step 3: Day trading alternative A: Buy and sell directly
You only need to click on the Trade Markets icon under Discover tab on your user dashboard.
This open up a window that in turn lists all the tradable assets on the platform, from cryptocurrencies to online stocks and forex pairs. Click on your preferred instrument to expose the buy and sell options and start trading.
Step 4: Day trading alternative B: Copy trades
You might want to use the copy trading feature if you are a day trading beginner, are a part-time trader with not enough time to analyze markets, or simply aren’t too confident of your win-loss ratio.
By copy trading, you are essentially copying the trade entry, trade exit, and risk management settings of some highly experienced traders with the lowest win-loss rations on the platform.
To copy trades, click on the Copy Trades icon under the Discover tab on your user Dashboard. It will open a window with a list of all the pro-traders whose trades you are allowed to copy.
Day Trading Buying Power and Account Minimums
Before you start day trading, ensure you are familiar with the following margin rules and account limits.
Day Trading – Day trading involves completing a round trip trade on the same day. If a trader buys security and then sells it on the same day, it is considered a day trade. Conversely, if a trader short-sells a security and buys it on the same day, it is considered a day trade.
Margin Trading – Most day traders borrow money from brokers to trade. Trading on margin involves using the money and securities in a brokerage account as collateral for the loan. How much the trader can borrow to trade is based on his risk profile and the value of the investment account (cash + securities). The ratio of the amount in the account to the amount borrowed is called leverage.
Pattern Trading – In the US markets, day traders are considered pattern traders if they borrow on margin, trade the same security four or more times within five business days, and day trading is six percent of the trade activity for that period. Once a day trader is considered a pattern trader, they are required to maintain a minimum balance of $25,000 to day-trade. This balance may be a combination of cash and securities. The pattern day trading rule does not apply to futures trading, making futures a popular day trading instrument.
Margin Call – If the value of the investment account falls below the maintenance margin, the trader will have several days to restore the account maintenance balance through cash and/or securities.
Leverage – Leverage is the buying power gained through margin lending expressed as a ratio of the amount in the account to the amount borrowed. If you have the $25,000 pattern trading minimum in your account and are allowed 4:1 leverage, you can borrow up to $100,000 to trade.
Day traders borrow money from brokers to trade on margin. This allows them to trade x times the value of their account (money + securities). A beginner trader may use 3 times leverage while an expert trader may secure up to 100 times leverage. Leverage not only magnifies potential investment gains but also potential losses.Glossary of Investment Terms
BondsA bond is a loan made to an organization or government with the guarantee that the borrower will pay back the loan plus interest upon the maturity of the loan term. It can be advanced to the national government, corporate institutions, and city administration. It is an investment class with a fixed income and a predetermined loan term.
Mutual FundA mutual fund is a professionally managed investment vehicle that pools together funds from numerous investors and invests it in such securities as stocks, bonds, and other money market instruments. They are headed by portfolio managers who determine where to invest these funds. They are highly regulated and invest in relatively low-risk money markets and in turn post lower rates than other aggressive managed funds.
P2P LendingPeer-to-peer lending (p2p lending) is a form of direct-lending that involves one advancing cash to individuals and institutions online. A P2P lending platform, on the other hand, is an online platform connecting individual lenders to borrowers.
BitcoinBitcoin is the legacy cryptocurrency developed on the Bitcoin Blockchain technology. It is a new form of money primarily developed to solve some of the inherent challenges associated with fiat currencies like inflation and over-production. It is virtual (online) cash that you can use to pay for products and services from bitcoin-friendly stores.
Index FundsAn index fund refers to the coming together of individuals to pool in funds that are then invested in the stock and money markets by professional money managers. The only difference between an index fund and a mutual fund is that the index fund follows a specific set of rules that track specific investments and index stocks.
ETFsAn Exchange-traded fund refers to an investment vehicle that is publicly traded in the stock exchange markets – much like shares and stocks. The fund is expert-managed and its portfolio comprises of such investment products as stocks, bonds, commodities, and more money market instruments like currencies.
RetirementRetirement refers to the time you spend away from active employment and can be voluntary or occasioned by old age. In the United States, the retirement age is between 62 and 67 years.
Penny StocksPenny Stocks refer to the common shares of relatively small public companies that sell at considerably low prices. They are also known as nano/micro-cap stocks and primarily include any public traded share valued at below $5.
Real EstateReal Estate can be said to be the land and buildings on a given property as well as other rights associated with the use of the property like the air rights and underground rights. Real estate can be either commercial if the land, property, and buildings are used for business purposes or residential if they are used to non-business purposes – like building a family home.
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)REITs are companies that use pooled funds from members to invest in income-generating real estate projects. While a REIT may specialize in one real estate niche, most diversify and invest in as many high-income real estate projects as possible. They are especially interested in commercial real estate projects like warehouses, prime office buildings, residential apartments, hotels, timber yards, and shopping malls.
AssetAsset simply refers to any resource of value or a resource that can be owned and controlled to produce positive value by an individual or business.
BrokerA broker is an intermediary to a gainful transaction. It is the individual or business that links sellers and buyers and charges them a fee or earns a commission for the service.
Capital GainCapital gains refer to the positive change in the price of a capital asset like shares and stock, bonds or a real estate project. It is the difference between the current selling price of the asset and its lower original buying price and it is considered a taxable income.
Hedge FundA hedge fund is an investment vehicle that pools together funds from high net worth individuals and businesses before having professional money managers invest it in highly diversified markets. The difference between mutual and hedge funds is that the later adopts highly complicated portfolios comprised of more high-risk high-return investments both locally and internationally.
IndexAn index simply means the measure of change arrived at from monitoring a group of data points. These can be company performance, employment, profitability, or productivity. Observing a stock index, therefore, involves measuring the change in these points of a select group of stocks in a bid to estimate their economic health.
RecessionA recession in business refers to business contraction or a sharp decline in economic performance. It is a part of the business cycle and is normally associated with a widespread drop in spending.
Taxable AccountsTaxable Account refers to any investment account that invests in shares and stocks, bonds and other money market securities. The account is offered by a brokerage company and you are obliged to report and pay taxes on the investment income each year.
Tax-Advantaged AccountsA tax-advantaged account refers to savings of investment accounts that enjoy such benefits as a tax exemption or deferred tax payment. Roth IRA and Roth 401K are examples of tax-exempt accounts whose contributions are drawn from after-tax incomes with the yields generated from investing funds therein being tax-exempt. Traditional IRA, 401K plan and college savings, on the other hand, represent tax-deferred accounts. Their contributions are deductible from your current taxable incomes but you get to pay taxes on their accrued incomes.
YieldYield simply refers to the returns earned on the investment of a particular capital asset. It is the gain an asset owner gets from the utilization of an asset.
Custodial AccountsA custodial account is any type of account that is held and administered by a responsible person on behalf of another (beneficiary). It may be a bank account, trust fund, brokerage account, savings account held by a parent/guardian/trustee on behalf of a minor with the obligation to pass it to them once they become of age.
Asset Management CompanyAn Asset Management Company (AMC) refers to a firm or company that invests and manages funds pooled together by its members. Like mutual or hedge funds, the AMC creates diversified investment portfolios that comprise of shares and stocks, bonds, real estate projects, and other low and high-risk investments.
Registered Investment Advisor (RIA)A registered investment advisor is an investment professional (an individual or firm) that advises high-net-worth (accredited) investors on possible investment opportunities and possibly manages their portfolio.
Fed RateThe fed rate in the United States refers to the interest rate at which banking institutions (commercial banks and credit unions) lend - from their reserve - to other banking institutions. The Federal Reserve Bank sets the rate.
Fixed Income FundA fixed-income fund refers to any form of investment that earns you fixed returns. Government and corporate bonds are prime examples of fixed income earners.
FundA fund may refer to the money or assets you have saved in a bank account or invested in a particular project. It may also refer to the collective basket of resources pooled from different clients that are then invested in highly diversified income-generating projects.
Value InvestingValue investing is the art of using fundamental analysis to identify undervalued shares and stocks in the market. It involves buying these shares at the current discounted prices and hoping that a market correction pushes them up to their intrinsic value effectively resulting in massive gains.
Impact InvestingImpact investing simply refers to any form of investment made with the aim of realizing financial returns while positively impacting the society, environment or any other aspect of life in the process. Investment in solar projects and green energy, for instance, posts profits and helps conserve the environment.
Investing AppAn investment App is an online-based investment platform accessible through a smartphone application. It lets you save and invest your funds in a preset portfolio that primarily consists of shares and stocks, bonds, ETFs, and currencies based on your risk tolerance.
Real Estate CrowdFundingReal Estate crowdfunding is a platform that mobilizes average investors – mainly through social media and the internet – encourages them to pool funds, and invests them in highly lucrative real estate projects. It can be said to be an online platform that brings together average investors and lets them enjoy real estate projects previously preserved for high net worth and institutional investors.
FAQs
How much do I need to start day trading?
In the US, day traders are considered pattern traders – traders who buy and sell the same securities four days within a five-day period. Pattern traders are required to maintain a minimum investment account balance of $25,000. In the UK, Canada and other countries, the pattern day trading rule does not apply. Each broker will have different account limits.
Do I need a margin account to day trade?
Most day traders use margin. The biggest mistake traders make is using the full margin allotment they are allowed. A beginner day trader should use a small fraction of the margin consistent with the trader’s risk profile.
Do I need to use stop-loss orders to day trade?
Stop orders are a popular way of limiting downside risk while trading. The two most popular are: Stop-loss order – Stops our the trade when the price reaches the determined amount. Trailing stop – Follows the price within a range (e.g. 10 pips). The trade is executed when the stock price passes through the target price.
I want to day trade binary options but the broker is not licensed in my country.
Because binary options have a high risk of loss, they are banned in many countries. In Europe, professional traders may trade them but they are off limits to retail traders. Anyone anywhere in the world can download a binary options broker app and start trading. If the broker goes out of business, your losses will not be covered by investment account insurance. Also be aware that many binary option dealers have been shut down owing to fraudulent activities.
If I stop day trading for more than five days, do I still need to maintain a $25,000 deposit?
According to the regulator FINRA, once an account is identified as engaging in pattern trader, they are typically required to maintain a $25,000 deposit.
See Our Full Range Of Trading Resources – Traders A-Z
Maggie Smith
Maggie Smith
Maggie is an investment expert with 10 years experience in dividend stocks and income investing. She has a PhD in Financial Markets and Investment Strategies and has contributed to a number of financial portals, writing stock market analysis pieces and reports on technology stocks and IPOs.View all posts by Maggie Smith
WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com