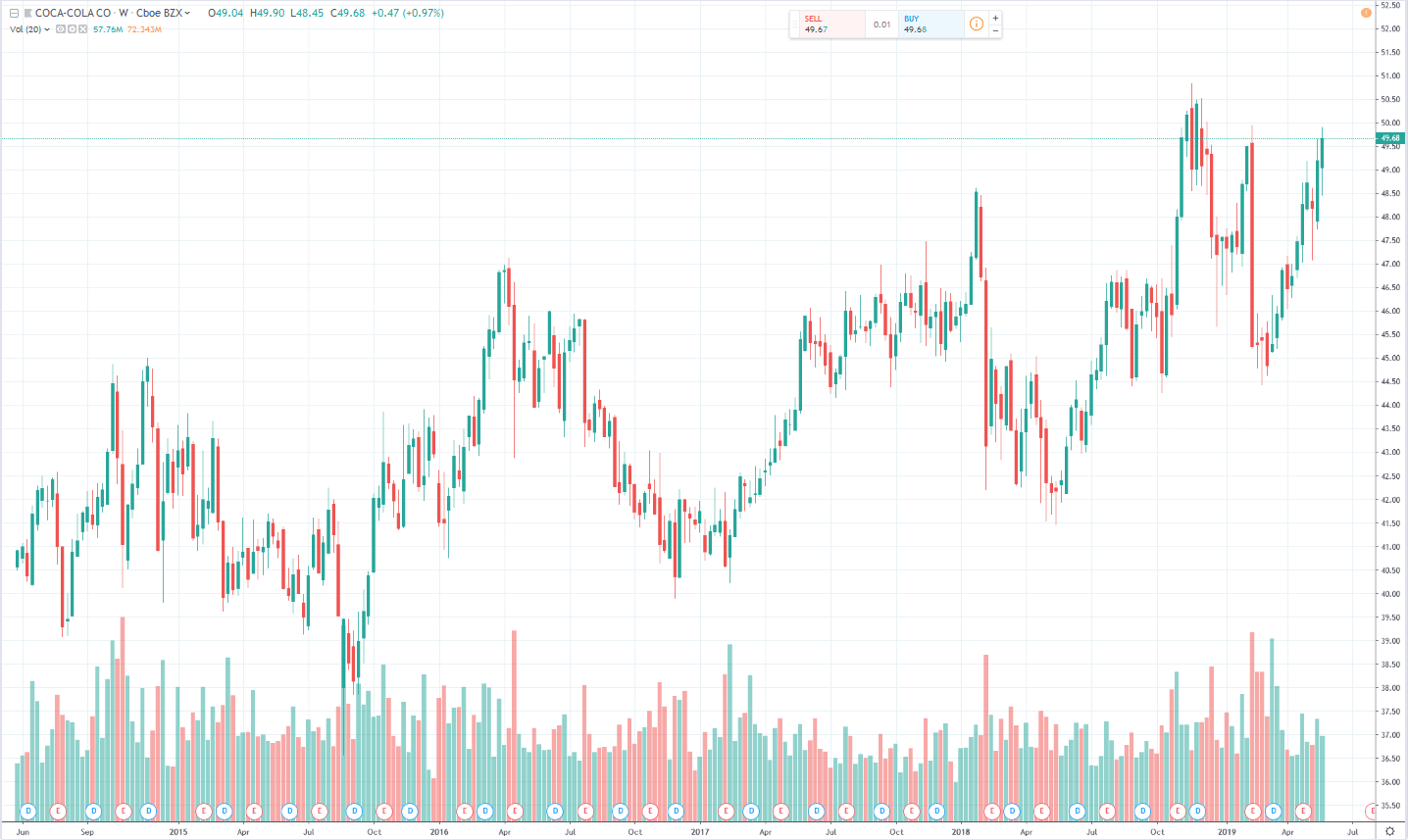
How to Buy Coca Cola Stock for Beginners
Every day there are news and events related to Coca Cola products and ads are constantly running to improve the popularity of the brand over Pepsi, its largest competitor.
Going by 2019’s financial report, the Company now focuses on energy drinks, coffee, and improved alternatives to traditional beverages.
In this piece, we will go over the basics of how to buy Coca Cola stocks safely, as well and how to determine the best online stock brokerage company
-
-
Where to Buy Coca Cola Stock
The industry is laden with stockbrokers claiming to be the best and who promise you the world.
To make the choosing process easier, we have compiled a list of the best stockbrokers in the US.
RECOMMENDED BROKER
What we like
- 0% Commission
- Trade Stocks Via CFDs
- Authorized & regulated by the FCA
Min Deposit
$100
Charge per Trade
Zero Commission
Available Assets
- Total Number of Stocks & Shares+2000
- US Stocks
- German Stocks
- UK Stocks
- European
- ETF Stocks
- IPO
- Funds
- Bonds
- Options
- Future
- CFDs
- Crypto
Charge per Trade
- FTSE 100 Zero Commission
- NASDAQ Zero Commission
- Dax Zero Commission
- Facebook Zero Commission
- Alphabet Zero Commission
- Tesla Zero Commission
- Apple Zero Commission
- Microsoft Zero Commission
Deposit Method
- Wire transfer
- Credit Cards
- Bank Account
- Paypal
- Skrill
Detailed provider overview
1. Plus500 – Coca Cola Stock Trading Through CFDs
Plus500 is a CFD trading platform founded in 2008. Plus500 provides trading services in CFDs in more than 2000 securities and assets, including forex, shares, ETFs, cryptocurrency, options, and commodities.
The difference between buying Coca Cola stock and Coca Cola stock CFD is that with stock CFD traders, you don't own the underlying assets. CFDs are simply a contract between you and Plus500.
Plus500 has its headquarters in the UK and, as such, has a license with the FCA. To provide additional security to your Coca Cola investment, it has licenses with CySec, ASIC, MAS, and FMA in Cyprus, Australia, Singapore, and New Zealand, respectively. Regulations by these bodies are strict and keep Plus500 honest with your investment.
Plus500 doesn't charge commissions. This means that when purchasing Coca Cola stock CFD, you will not pay brokerage fees that other companies charge for making investments through their platforms. However, Plus500 has spreads, which are the price difference between the selling and buying price of the stock CFD. And though with some brokers it means added trading costs, Plus500 has low spreads which translate into a higher profit margin for you.
Also, to get you started on learning the ropes, Plus500 offers a demo account with no time limit. In this account, you can practice strategies you'll use on real Coca Cola stock CFD trading without losing a dime.
All this trading takes place on a proprietary trading platform (Webtrader). Plus500 offers a desktop version and mobile version that work seamlessly together. If you ever need help with your Coca Cola stock CFD, you can contact their friendly customer support that is available 24/7.
Our Rating
- Low spreads
- Regulated by ASIC, MAS, CySEC, FCA
- Has over 2000 CFD products
- Limited research resources and tools
- Doesn't have the MetaTrader 4 platform
80.5% of retail CFD accounts lose money. Sponsored ad2. Stash Invest – Best USA Broker
Stash Invest is a micro-investing app that started in 2015. The platform was created to help increase the number of US citizens investing in stocks. They achieve this goal by reducing the initial investment amount. With as low as $1, you can access Stash Banking and a basic brokerage account.
Aside from Coca Cola stock, there are lots of other companies that you can invest in. But to help keep things light and manageable, Stash Invest reduces the investment options to 450 stocks and ETFs. As such, building an investment portfolio around your Coca Cola stocks is easier.
As part of reducing the cost of your KO investment, Stash Invest offers fractional shares. This means that Stash Invest buys full Coca Cola stock and then splits them into small stocks depending on what you can afford. Fractional shares allow you to diversify your portfolio and improves financial flexibility.
And as if that's not enough, Stash Invest offers a $5 welcome bonus when you sign up to give you a head start on your Coca Cola stock investment. And to ensure your success, Stash Invest offers comprehensive guidance and investment lessons, including how to manage your KO portfolio and how to trade. It's also ideal for long-term investors as it teaches them how to be patient and watch the rise and fall of KO stock prices.
Our Rating
- $0 minimum balance
- Allows fractional stock purchase
- $1 as the monthly fee
- The number of shares isn't as many in comparison to other brokers
- It doesn't have investment management
- You need $9 a month to unlock complete features
Sponsored adHow to Buy Coca Cola Stock
Assuming you have a funded account, below are the simple steps to take buy Coca Cola stock.
Note: you need to verify your account to lift the deposit limit on your account.Step 1: Search for Coca Cola (KO) Stock
Step 2: Click on trade
Step 3: Specify ‘Buy’
Specify ‘Buy’ on the top tab, change the leverage to X1 to purchase real stock and proceed to set your order. At the time of this purchase the market was closed and it was a weekend (as seen on screenshot two above). As such, there was an extra fee for the convenience of trading outside normal hours. And if at this point you haven’t put money into your account, you’ll be prompted to do so.
Why Invest in Coca Cola?
Coca Cola has a rich history laden with its fair share of ups and towns. But today, it’s one of the largest companies in the world. But in stock investments, the past counts for little as opposed to the present and the future of the company and the stock. With that in mind, here is what you need to know.
Coca Cola stock has capital appreciation
Over the years, Coca Cola has continually paid average returns with regards to the S&P 500 Index. However, your gains will fluctuate depending on the stock price when you make a purchase.
Quarterly dividend
Currently, Coca Cola pays its stakeholders a dividend of $0.40 for every share. This translates to about $1.60 a year, which translates to a 3.1% yield on your stock. In comparison to a 30-year Treasury yield at 2.85%.
Defensive stock
Coca Cola is a defensive stock. With the current state of the business cycle, investing in a defensive stock can be popular. If ever the US economy takes a dip, your investment would be protected to an extent.
Positive Long-Term Outlook
Even though it’s not good to judge future results from past performance of a company, provided you buy Coca Cola stock at a great price when the market plunges, you will enjoy capital appreciation in the long run.
About Coca Cola Stock
Company and stock history
Coca Cola’s history dates back to 1886 when Dr. John S. Pemberton, an Atlanta Pharmacist, created what would later grow into the world’s largest soft drink brand. Dr. John made a flavoured syrup, which he mixed with carbonated water and put on shelves for $0.05 a glass. In the first year, he sold about nine glasses a day. Today, Coca Cola sells about 1.9 billion servings a day. Dr. Pemberton passed on to years later, but he had sold parts of his company to investors.
The company became the Coca Cola Company in 1902. The original Coca Cola NYSE symbol was CCO, but it later changed to KO (still in use). According to a statement made in 2012 by the company, a single Coca Cola company share bought for $40 in 1919 would be worth $9.8 billion in 2012 if the dividends were reinvested over the years.
Note: This is a compound annual growth rate of +14.27 in close to a century.Coca Cola Stock
The defensive stock market is made up of companies that deal with consumer staples like beverages, food, household products, and tobacco. These stocks can usually remain valuable even when the economy takes a dip and other stocks are sold.
But on the other hand, cylindrical stocks, including companies in the industrial, insurance, banking, building, and automotive industries, lose value when the economy takes a dip.
Being a defensive stock, Coca Cola is resilient to the changes in the markets. Moreover, Coca Cola pays quarterly dividends of $0.40. This value has been on an uptrend for the past 57 years and is a representation of a 3.22% yield.
Coca Cola’s business model
Its business model revolves around the sale and distribution of the syrup concentrates it manufactures. The syrups are converted into Coca Cola and other soft drinks when they are mixed into carbonated water.
Therefore, the company generates revenues from the sale of concentrates and finished products sold. The syrup is sold to authorized franchisees and bottlers, which then sell it to the end consumer under the Coca Cola brand. Its most popular flavours include Sprite, Fanta, Coca Cola, or any other depending on the franchisee.
The finished products sold directly by the company fall under B.I.G (Bottlers Investment Group), which was made to ensure that the franchisee business is a success all over the world.
Note: BIG works by placing some bottlers under temporary direct ownership of the brand and allowing them to use the resources available to fuel long term growth.Conclusion
For the longest time, the Coca Cola stock has been a part of the Berkshire Hathaway’s holding. And so far, there is no indication that the investment firm is willing to sell its stocks soon. And this adds further weight to the stock, especially when you consider Buffett’s eye for prestigious stocks.
Glossary of Stocks Terms
StockA stock is a representation of a company’s equity. When a company wants to raise capital, it issues stocks to the public. It is the aggregation of the total stocks owned by one individual that inform their shareholding of the company.
SharesA share is an indivisible unit of capital that expresses the ownership relationship between a shareholder and a particular company, mutual fund, REITs or limited partnership. A share indicates a portion of ownership (claim) that one has on a company or fund.
DividendDividend refers to the portion of the company’s profits that is distributed to its stockholders. It can be on a quarterly or annual basis.
Bull marketA bull market is an economic condition where the stock markets are in an extended period of consistent increase in stock prices.
Bear MarketA stock market is said to be bearish if it is involved in extended periods of continuous price decrease of the stock prices.
Stock ExchangeA stock exchange is an institution or a platform where shares and stocks and a host of other money market instruments are traded.
Return On Investment (ROI)The return on investment is the profit you make from trading in or investing in shares and stocks of a particular company. It often comes from selling the investment at a higher price than was originally bought or benefiting from dividends and other profit-sharing schemes as a result of owning and holding onto a particular investment.
BrokerA broker may be a person or entity that engages in the buying and selling of different types of investments on behalf of other individuals or entities at a fee (or commission).
Day TradingDay Trading is the practice of buying a money market investment product and selling it as soon it reports price increase or loss, within the same day. Traders engaged in day trading are referred to as “day traders” or “active traders”
ArbitrageArbitrage is the act of buying and selling security at different stock exchanges or markets with varying prices. If, for instance, stock ABC sells at $11 on one exchange and $11.75 on the other, arbitraging involves buying from at the low price exchange and profiting by selling it at the higher-priced exchange.
IndexA stock index is a statistical measure of the change in the stock and securities market. It comprises a hypothetical portfolio of different companies whose change in prices is calculated to determine market performance.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)The Initial Public Offering refers to the sale of company stock to the public for the first time. It is the act of taking a company public and is highly regulated by such financial regulators like the SEC in the USA and FCA in the UK.
OptionsOptions are derivative financial instruments whose price is based on the value of their underlying tradable security like shares and stocks. They are contracts that give the holder an option to buy or sell the underlying asset at a later date. Unlike futures, an options contract holder has the choice to buy/sell or not.
Call optionsThis is an options contract that gives the holder an option to buy the underlying asset before the expiry date.
Sell optionsThis option gives its holder the choice of selling the underlying asset before its expiry date
Mutual FundsA mutual fund refers to a company that pools funds from different investors and invests these funds in stocks, bonds, and other financial market securities. They then distribute the capital gains from these invests to their members.
Over-the-CounterThe process through which stocks for companies that are not listed with accredited stock exchanges like the NYSE are traded. It is a broker-dealer network for unlisted stocks for companies that do not meet listing requirements set by the organized exchanges.
OverboughtA stock is said to be overbought if it is traded excessively over a short period of time and at unjustifiably high prices.
OversoldA stock is said to be oversold if it is consistently traded below its true value.
Ask PriceAlso referred to as the offer or asking price, this refers to the lowest price that the seller will take for a stock.
Bid PriceBid price refers to the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a stock.
VolumeIn the stock trading context, Volume refers to the number of shares that change hands within a given period of time, be it a day, month or annually. It is trading/investment indicator where rising trade volumes point to a healthy stock while dwindling volumes are indicators of investor pessimism towards a stock.
VolatilityRefers to the statistical measure of the change in price of a stock over a given period of time. It is a measure of the rate and the time it takes for a stock price to move from high to low and how long it remains within a certain price range. The higher the volatility, the higher the risk.
52-Week HighThis refers to the highest closing price recorded by a given stock in the last 52 weeks.
52-Week LowThis refers to the lowest closing price that a particular stock recorded in the last 52 weeks.
Bid-Ask SpreadThe bid-ask spread refers to the difference between the lowest price that a seller is willing to take for their stock and the highest price that a buyer is willing pay for the stock. It is the difference between the quoted ask and bid prices.
Market OrderA market order is an instruction by an investor to the broker or brokerage platform asking them to buy/sell a stock or any other security at the best price available at that moment. It is often issued when an investor wishes to enter or exit the market quickly and at the prevailing rates.
Limit OrderA limit order is an order that triggers a sale or buy when a predetermined or better price is met. For a buy limit order, the buy order is executed once the set limit price or a better price is triggered. The sell limit order on the hand triggers the sale of stocks if the limit price or better price is hit.
Stop OrderAlso referred to as a stop loss order, it is an order that triggers a buy or sell action once a predetermined price level is hit. It is designed to help you minimize possible loss on a given trade should the markets move against your bet.
Take ProfitTake profit is a type of limit order dictating the price level at which the broker or brokerage platform is to close a trade for profit.
Capital GainsCapital gain refers to the value rise of a tradable financial instrument that makes its selling price higher than the buying price. It can also be referred to as the profit realized from liquidating a capital investment like stocks.
ETFsAn ETF is a collection of many tradable instruments like bonds, stocks, and commodities. These are listed on the exchanges and traded like ordinary stocks.
Debt-to-Equity RatioThe debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio is a financial ration tool used to measure the financial health of a company by gauging value of its equity in relation to debt. It is achieved by dividing the company’s total liabilities in relation to its shareholder’s equity.
Dividend InvestingThis is an investment strategy where the investor only buy shares that have consistently paid out high dividends in the past or others with the fastest dividend rates. Dividend investing strategy advocates are more interested in how much a shares pays in dividends than its price fluctuations.
Growth StocksGrowth stocks refers to the stocks of companies that are expected to grow at a faster rate than the industry average and report consistent and sustainable cashflows. The company sales and revenues are also expected to increase at a faster than that of an average company in the same industry.
Penny StocksThese are also referred to as micro-cap or nano-cap stocks and refers to the stocks of relatively small companies valued less than $5 and only trade via the Over-The-Counter markets.
Blue ChipA blue chip refers to a nationally recognized and financially sound company with a long and stable record of consistent growth. It is company whose financial might and nature of operation make it well suited to face turmoil and remain profitable in the uncertain economic conditions..
Short SellingShort selling is a trade/investment strategy where the investor is banking on the decline of the shares of a particular company. They therefore borrows these shares, sells them at the current market price and buys them back after they lose value, effectively profiting from the price difference.
YieldYield refers to the profit/earnings generated from investing in a particular stock or market instrument over a given period of time and is expressed a percentage of the stock’s market value, face value or as percentage of invested amounts.
Capital StockCapital stock, also referred to outstanding shares, refers to all the regular shares issued by a company and held by all its shareholders including the restricted/locked-in shares held by company insiders, executives, and institutional investors. The number of capital stock is used in calculating key metrics including cash-flow per-share and earnings per share.
Earnings Per Share (EPS)EPS refers to the monetary value, the profit or earnings attributable to each outstanding shares held by a company. It is a financial ratio that is arrived at by dividing the company’s profit by its outstanding shares of the common stock.
Price Earning Ratio (PER)Also referred to as Price-to-earnings ratio, PER is a financial metrics tools used to check if a company’s shares are over/undervalued by dividing the shares current market price with its earnings-per-share.
FloatA company’s flat refers to the number of regular shares issued to investors that are available for trading. The float shares figure is arrived at by subtracting the locked-in shares held by company insiders and executives from its capital stock.
Gap-up StocksGap up stocks refer to company stocks that open the day trading at relatively higher prices than their previous day’s closing price. This is often attributed to the after-market trading activity.
Gap-Down StocksGap down stocks refers to company stocks that open the day trading at relatively lower prices that the previous day’s closing price. For instance if a company stock closes the day trading at $50 but opens the following day trading at $45, it is said to have a 5-point gap down.
Stock BuybackStock buyback, also referred to as share repurchase, occurs when a publicly listed corporation uses a part of its revenues to buy back its shares from the marketplace. The move effectively reduces the number of company shares in circulation, which translates to an increased share price.
HOLDHOLD is a financial recommendation issued by a qualified financial institutions or financial analyst advising investors/traders not to buy or sell a particular stock. It is a no-action situation where long position traders are advised not to sell and others investors advised not to buy into the stock.
Resistance LevelsThis refers to the upper-most price level that a particular stock or any other security reaches but doesn’t exceed due to dwindling number of buyers and an increasing number of sellers.
MacroeconomicIs a branch of economics that’s concerned with the study of how the economy and different large-scale markets are structured, how they behave, and how they perform.
RSIRelative Strength Index is a technical momentum indicator used in market analysis to determine if a stock is overbought or oversold by measuring the magnitude of a recent bullish or bearish price run. It has a scale of 0-100 where RSI readings of 70+ indicate a stock is overbought while an RSI reading below 30 is an indicator of an oversold security.
Moving AverageMoving Averages is a statistical calculation that is specially designed to identify the arithmetic mean of a given number of data sets or range of prices calculated over a given period of time. Each of these data set or price range is created by the average/mean price for that subset. For instance, a single data point on a moving averages scale may represent the average stock price for a day or trading session.
Bollinger BandsBollinger Bands are a technical indicator tool characterized by two statistical carts that run alongside each other indicating the changes in prices and volatility of a financial instrument like stock or commodity over a given period of time.
Fibonacci RetracementsFibonacci retracements refer to two horizontal lines that use the Fibonacci numbers to measure the percentage of price retracement in a bid to indicate where the resistance and support are most likely to occur.
FAQ
How many people has Coca Cola employed?
According to the latest data, it has 86,200 workers
When does Coca Cola’s fiscal year-end?
The fiscal year ends in December
Where is Coca Cola located?
Its address is One Coca Cola Plaza 30313, Atlanta USA
Does Coca Cola have an ISIN number?
Yes, it does. It is US1912161007
How much was Coca Colas share when it first went public?
The shares went for $40 per share. During its life, the stocks have split about 11 times.
Who owns the biggest shares in Coca Cola?
Buffet doesn’t shy away from sharing his affection for the Coca Cola Company. Berkshire Hathaway owns most of the shares (400 shares). Buffet drinks five cokes a day.
Thadues
Thadues
View all posts by ThaduesThadeus Geodfrey has been a contract writer for Lernbonds since 2019. As a fulltime investment writer, Thadeus oversees much of the personal-finance and investment-planning content published daily on this site. With a background as an iGaming expert and independent financial consultant, Thadeus’s articles are based on years of experience from all angles of the financial world.
WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site.
Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com