Bond Convexity: The Relationship Between Bond Yields and Interest Rates
If you’ve mastered the ins and outs of how bonds work, things are about to get a lot more complicated; bond convexity. In a nutshell, the convexity of a bond refers to the relationship between bond yields and interest rates.
Although not an exact science, if the ‘duration’ on a bond increases and the yield falls, bonds have a positive convexity. Similarly, if the yield increases and the duration falls, its convexity is negative.
Confused?
If so, we would suggest reading this in-depth guide on bond convexity. We explain in plain English what bond convexity is, how it works, and how financial institutions can mitigate the risks of a bond investment by analyzing its convexity.
Featured Bonds Broker 2020 The bond convexity goes one step further than simply measuring the relationship between interest rates and yields, as it also takes into account the bond’s duration. The duration measures the sensitivity of an asset in relation to external market forces, such as interest rates. So, in order to understand how the convexity of a bond actually works, and why it’s a crucial tool in mitigating your risks, we need to first understand its influencing factors. This includes: If you’re here reading an advanced topic like bond convexity, then it’s likely that you already have a firm grasp of how bond yields work. With that said, the yields of a bond can play a major role in determining its convexity, so let’s recap. If you’re confused by the fact that bond yields increase when the risk goes up, think of it like this. If you were buying US Treasury bonds with a fixed yield of 3%, but the risk of default had increased, would you be happy getting the same 3% that investors got when they were first issued? No, because you would want to receive a higher return to reflect the increase in risk. As such, by demanding 4% instead of the fixed coupon rate of 3%, the yield has increased. So now that we’ve covered bond yields, we need to look at how interest rates have a major influence on the value of bonds, and in turn, its convexity. To clarify, we are referring to the interest rates set by central banks like the Federal Reserve, Bank of England, and European Central Bank. How does this impact bonds? Well, when interest rates go up, the yield on bonds will go up, meaning they are worth less than what you originally paid. For example, let’s say that you have US government bonds at a yield of 2%. If the Federal Reserve then increases interest rates, it will force the value of the bond yield to go up, let’s say to 3%. This means that because investors will now get a yield of 3% on newly issued bonds, they won’t be interested in your 2% bonds. As such, the value of your bonds would go down as you would be required to sell them at a discount. The same is true when government interest rates go down but in reverse. The final piece of the puzzle in understanding bond convexity is the bond duration. This is where things start to get a bit more complicated, as being able to calculate the duration of an asset requires highly advanced mathematical modelling, much like the convexity. With that said, let’s explain the basics. Ultimately, the higher the bond duration, the higher the risks for the investor. This is because the bonds will react in a more volatile manner if interest rates change. However, the convexity goes one step further by exploring how both the bond price and bond duration will change when interest rates go up or down. In doing so, this allows financial institutions to gauge how much risk their government bond portfolios present. Interestingly, the convexity of a bond can be either positive or negative. If the convexity of a bond is positive, the following conditions are typically in play: As you can see from the above example, if the bonds have a positive convexity, they will increase in value at a faster rate (2%) when interest rates go down, compared to the rate of decline when rates go up (1.5%). In Layman’s Terms, you as the bondholder will experience more gains when the yield falls, than you will lose when the yield increases. If a bond has a negative convexity, it operates much like its positive counterpart, but in reverse. This means that: As per the above example, a negative convexity will see the bonds decline at a much faster rate (2%), compared to the respective rate (1.5%) of an increase. In short, if you’re an everyday retail trader buying and selling bonds on a DIY basis, it’s highly unlikely that you will have the necessary tools to calculate the bond convexity. This is because such calculations are based on highly advanced mathematical models. Financial institutions and hedge funds are well versed in the convexity of bonds, as they have the required resources to assess this at the click of a button. With that said, it is important to remember that the specific bond convexity is nothing more than speculation. By this, we mean that there is no sure-fire way to know how much a bond will change in value in relation to an increase or decrease in interest rates. After all, the financial markets can be irrational at times. We hope that by reading our guide from start to finish, you now have a firm understanding of what the convexity of a bond is. As we have discussed in great depth, you will first need to get to grips with three key metrics in order to understand convexity. This includes the bond yield, bond duration, and how the movement of government interest rates can impact the value of a bond. Once you’ve got your head around these three metrics, you can begin to unravel what a positive or negative bond convexity looks like. With that being said, calculating the bond convexity is best left to large-scale financial institutions who have the required mathematical models. Featured Bonds Broker 2020 Bond convexity looks at the relationship between interest rates and the bond duration. That is, the rate that the bonds will increase or decrease when interest rates move. If the convexity of a bond is positive, it means that the bond duration increases as the yield falls. If the bonds have a negative convexity, then the duration of the bond increases as the yield rises. Yes, there is a direct relationship between the market value of government bonds and the central bank interest rate. In the vast majority of cases, the value of a bond will go down as interest rates go up. Similarly, the value of the bond will go up as interest rates decrease. People often confuse the bond duration with the maturity date of the bond. However, it actually relates to the sensitivity of the bond price in relation to a potential change of interest rates. Financial institutions and hedge funds attempt to measure the bond convexity to asses how risky they are. More specifically, they seek to understand how the value of the bonds will move in response to a change in interest rates. Kane holds academic qualifications in the finance and financial investigation fields. With a passion for all-things finance, he currently writes for a number of online publications. WARNING: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing your capital is at risk. This site is not intended for use in jurisdictions in which the trading or investments described are prohibited and should only be used by such persons and in such ways as are legally permitted. Your investment may not qualify for investor protection in your country or state of residence, so please conduct your own due diligence. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice. This website is free for you to use but we may receive commission from the companies we feature on this site. Copyright © 2026 | Learnbonds.com


What is Bond Convexity?
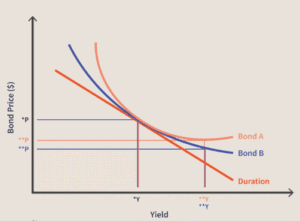
Bond Yield
Interest Rates
Bond Duration
How Does Bond Convexity Work?
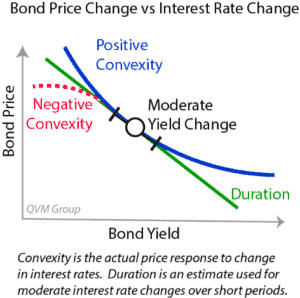
Positive Bond Convexity
Negative Bond Convexity
Should I Attempt to Calculate the Bond Convexity?
Conclusion


FAQs
What is bond convexity?
What is a positive bond convexity?
What is a negative bond convexity?
Do interest rates impact the value of bonds?
What is the bond duration?
Why does the bond convexity matter?
See Our Full Range Of Bonds Resources – Bonds A-Z
Kane Pepi


